Spire.XLS 14.6.6 supports converting Excel to Markdown format
We're pleased to announce the release of Spire.XLS 14.6.6. This version supports converting Excel to Markdown format, and fixes some issues that occurred when converting Excel to image/HTML, and adding filter to Excel PivotTable. More details are shown below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | - | Supports converting Excel to Markdown format.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");
workbook.SaveToFile("output.md",FileFormat.Markdown);
|
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5191 | Fixes the issue that the application threw "ArgumentOutOfRangeException" when setting "horizontal" and "vertical" type borders. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5243 | Fixes the issue that the effect was incorrect when calling "Worksheet.Activate()" method. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5262 | Fixes the issue that the text content layout was incorrect when converting Excel to image. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5265 | Fixes the issue that the comment order in Excel was incorrect after sorting. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5269 | Fixes the issue that the font effect was incorrect when converting Excel to Html. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5272 | Fixes the issue that an error prompt appeared when opening the result document after adding a filter to an Excel PivotTable. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5273 | Fixes the issue that the cell color was lost when converting Excel to Html. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5283 | Fixes the issue that the cell icons were lost when converting Excel to Html. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5217 | Fixed the issue that the "Worksheet.SetLastRow()" method did not take effect. |
Python: Sort Data in Excel
When working with large amounts of information, the ability to quickly sort data can be very beneficial at times. By arranging data in ascending, descending, or customized order, users can easily spot trends, analyze relationships, and extract valuable insights. In this article, you will learn how to sort columns or rows in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Sort By Columns in Excel in Python
- Sort By Custom List in Excel in Python
- Sort By Rows in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Sort By Columns in Excel in Python
The Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(key: int, sortComparsionType: SortComparsionType, orderBy: OrderBy) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python allows users to sort data based on different criteria. For example, you can sort cell values, cell colors or font colors in ascending, descending, or other order.
The following are the steps to sort the values in a specified column:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Specify the sorting mode using Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add() method.
- Sort data in a specified cell range using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Budget.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
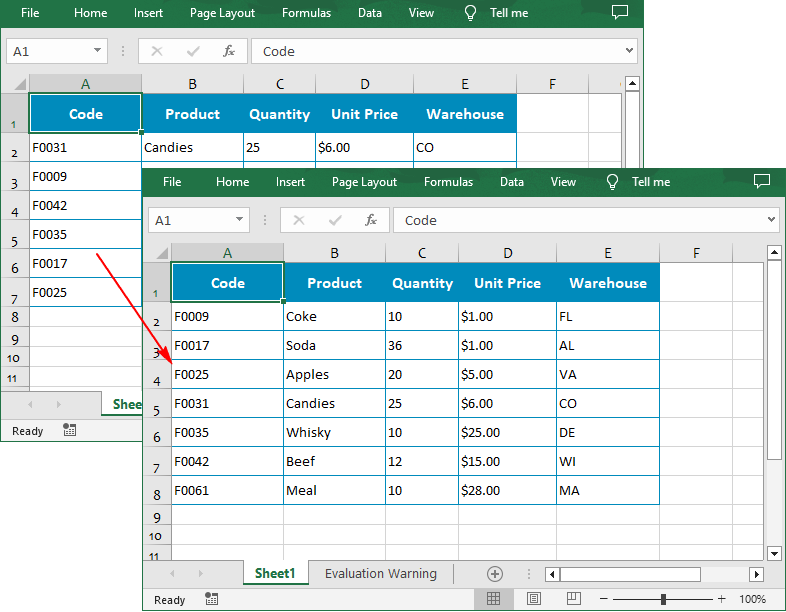
# Sort values in the specified column in ascending order
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(0, SortComparsionType.Values, OrderBy.Ascending)
# Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(worksheet["A1:E7"])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("SortByColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Sort By Custom List in Excel in Python
You can also create a custom list and then sort data based on it using the Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(key: int, customSortOrder: List[str]) method.
The following are the steps to sort data using a custom list:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Create a custom sort list, and then sort a specified column using it though Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add() method.
- Sort data in a specified cell range using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Budget.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
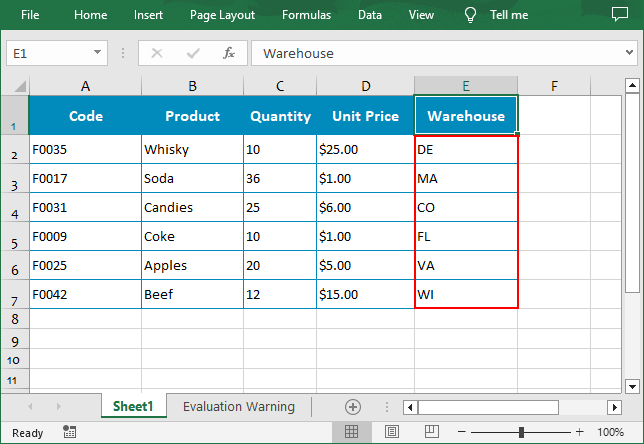
# Create a custom sort list
customList = ["DE","MA", "CO", "FL", "VA", "WI"]
# Sort a specified column using the custom list
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(4, customList )
# Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(worksheet["A1:E7"])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("CustomSortList.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Sort By Rows in Excel in Python
To sort a specified row in Excel, you need to set the sort orientation to LeftToRight, specify the sort mode and sort row data accordingly.
The following are the steps to sort the values in a specified row:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set whether to include titles when sorting using Workbook.DataSorter.IsIncludeTitle property.
- Set the sort orientation using Workbook.DataSorter.Orientation property.
- Specify the sorting mode, and then sort data in the first row using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort(Worksheet.Rows[0]) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Year.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set whether to include titles when sorting
workbook.DataSorter.IsIncludeTitle = True
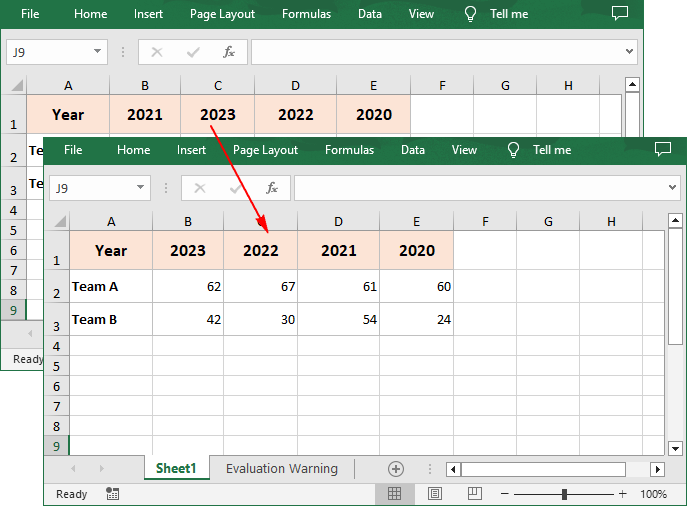
# Set the sort orientation
workbook.DataSorter.Orientation = SortOrientationType.LeftToRight
# Specify the sorting mode
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(0,SortComparsionType.Values,OrderBy.Descending)
# Sort data in the first row
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(sheet.Rows[0])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("SortByRows.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Spire.Doc 12.6.10 supports loading customized font replacement rules in XML format for conversion
We are excited to announce the release of Spire.Doc 12.6.10. This version supports loading custom font replacement rules in XML format for conversion and saving the XML of the document's default font replacement rules. Besides, it enhances the conversion from Word to PDF and HTML to Word. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | - | Adds the Document.SaveFontFallbackRuleSettings() method to save the XML of the document's default font replacement rules.
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile);
document.SaveFontFallbackRuleSettings("FontReplacementRuleSettings.xml");
|
| New feature | - | Adds the Document.LoadFontFallbackRuleSettings() method to load custom font replacement rules in XML format for conversion.
Document document = new Document(); document.LoadFromFile(inputFile); document.LoadFontFallbackRuleSettings(“CustomFontReplacementRuleSettings.xml”); document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF); |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10425 | Fixes the issue that the program threw "System.ArgumentNullException" error when converting Word documents to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10544 | Fixes the issue that the images were not displayed after converting HTML to Word. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10554 | Fixes the issue that images and hyperlinks were incorrect after converting Markdown to Docx. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10587 | Fixes the issue that the program threw "Unknown boolex value" error when converting Word to PDF. |
Spire.PDF for Java 10.6.2 enhances the conversion from PDF to OFD and images
We are delighted to announce the release of Spire.PDF for Java 10.6.2. This version enhances the conversion from PDF to OFD and images and SVG to PDF. Besides, some known issues are fixed successfully in this version, such as the issue that an error "StringIndexOutOfBoundsException" was thrown when extracting PDF tables. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6767 | Fixes the issue that an error "StringIndexOutOfBoundsException" was thrown when extracting PDF tables. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6781 | Fixes the issue that text was overlapped after converting PDF to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6796 | Fixes the issue that an error "Width (48) and height (0) must be > 0" was thrown when compressing PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6810 | Fixes the issue that bookmarks were lost after converting PDF to OPD. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6821 | Fixes the issue that content was lost when converting SVG to PDF. |
Python: Set the Number Format for Excel Cells
Setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets is crucial for data management and presentation, which enhances readability, ensures consistency, and facilitates accurate data analysis. Proper number formatting allows users to distinguish between different types of numerical data, such as currency, percentages, dates, and scientific notations, making complex datasets more comprehensible at a glance. In this article, we will explore how to automate the process of setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets with Spire.XLS for Python in Python programs.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set the Number Format for Cells in Excel Worksheets
In an Excel workbook, the number format of a cell is determined by its format code. Developers can utilize various symbols in format code to define how numerical data, date and time, currency, etc. are displayed. Below are some commonly used symbols in number format codes:
- #: Represents a digit placeholder that displays only non-zero digits.
- 0: Represents a digit placeholder and always occupies at least one position.
- ; (semicolon): Separates formats for positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero.
- / (slash): In date formats, separates year, month, and day.
- $: Currency symbol, used for representing monetary values, adaptable to system regional settings.
- () (parentheses): Formats negative numbers by enclosing them in parentheses.
- [ ] (square brackets): Utilized in conditional formatting, such as color settings [Red] or conditions like [<=100]"Low";[>100]"High".
Spire.XLS for Python provides the CellRange.NumberValue property to set the number value of a cell and the CellRange.NumberFormat property to set the number format with format code. Below are the steps for setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets with Python:
- Create an instance of Workbook class to create an Excel workbook.
- Get the first default worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Add text to header row through Worksheet.Range[].Text property.
- Add number value to cells through Worksheet.Range[].NumberValue property and set the number format for the cells with format code through Worksheet.Range[].NumberFormat property.
- Save the Excel workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Set the header row
sheet.Range["B9"].Text = "Number Format"
sheet.Range["C9"].Text = "Value"
sheet.Range["D9"].Text = "Display"
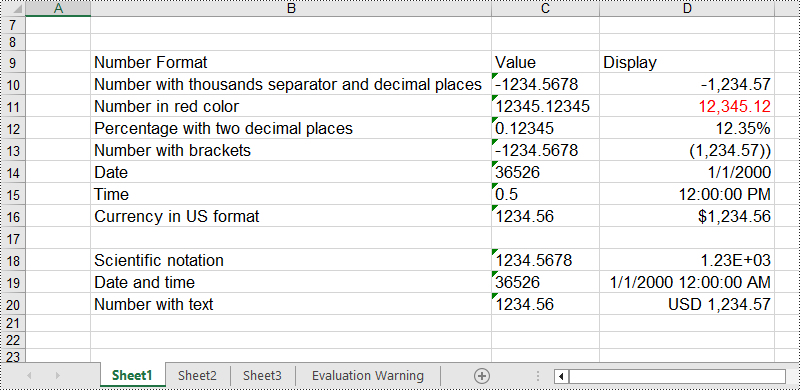
# Number with thousands separator and decimal places
sheet.Range["B10"].Text = "Number with thousands separator and decimal places"
sheet.Range["C10"].Text = "-1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberValue = -1234.5678
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberFormat = "#,##0.00"
# Number in red color
sheet.Range["B11"].Text = "Number in red color"
sheet.Range["C11"].Text = "12345.12345"
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberValue = 12345.12345
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberFormat = "[Red]#,##0.00"
# Percentage with two decimal places
sheet.Range["B12"].Text = "Percentage with two decimal places"
sheet.Range["C12"].Text = "0.12345"
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberValue = 0.12345
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberFormat = "0.00%"
# Number with brackets
sheet.Range["B13"].Text = "Number with brackets"
sheet.Range["C13"].Text = "-1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberValue = -1234.5678
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberFormat = "(#,##0.00;(#,##0.00))"
# Date
sheet.Range["B14"].Text = "Date"
sheet.Range["C14"].Text = "36526"
sheet.Range["D14"].NumberValue = 36526
sheet.Range["D14"].NumberFormat = "m/d/yyyy"
# Time
sheet.Range["B15"].Text = "Time"
sheet.Range["C15"].Text = "0.5"
sheet.Range["D15"].NumberValue = 0.5
sheet.Range["D15"].NumberFormat = "h:mm:ss AM/PM"
# Currency in US format
sheet.Range["B16"].Text = "Currency in US format"
sheet.Range["C16"].Text = "1234.56"
sheet.Range["D16"].NumberValue = 1234.56
sheet.Range["D16"].NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00"
# Scientific notation
sheet.Range["B18"].Text = "Scientific notation"
sheet.Range["C18"].Text = "1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D18"].NumberValue = 1234.5678
sheet.Range["D18"].NumberFormat = "0.00E+00"
# Date and time
sheet.Range["B19"].Text = "Date and time"
sheet.Range["C19"].Text = "36526"
sheet.Range["D19"].NumberValue = 36526
sheet.Range["D19"].NumberFormat = "m/d/yyyy h:mm:ss AM/PM"
# Number with text
sheet.Range["B20"].Text = "Number with text"
sheet.Range["C20"].Text = "1234.56"
sheet.Range["D20"].NumberValue = 1234.5678
sheet.Range["D20"].NumberFormat = "\"USD \"#,##0.00"
# Set the font size and autofit rows and columns
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.Font.Size = 13
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows()
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SetNumberFormatExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#: Add, Modify, or Remove Word Table Borders
Adding, modifying, and removing Word table borders can enhance the readability, aesthetics, and organization of data. Adding borders makes the content of the table clearer, distinguishing between different cells, which helps readers quickly identify information. Modifying border styles (such as line thickness, color, or pattern) can emphasize key data, guide visual flow, or conform to specific document styles and design requirements. Removing borders, in some cases, reduces visual clutter, making the content more compact and minimalist, especially suitable for data presentation where strict divisions are not needed or when you wish to downplay structural visibility. This article will introduce how to add, modify, or remove Word table borders in C# projects using Spire.Doc for .NET.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
C# Add Word Table Borders
To set borders for all cells in an entire Word table, you need to iterate over each cell and set its visual border properties. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Use the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load a document.
- Retrieve the first section of the document using Document.Sections[0].
- Get the first table in that section by using Section.Tables[0].
- Use a for loop to iterate through all the cells in the table.
- Set TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.BorderType to BorderStyle.Single, which sets the cell border to a single line style.
- Set TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.LineWidth to 1.5, defining the border width to be 1.5 points.
- Set TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.Color to Color.Black, setting the border color to black.
- Save the changes to the Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("TableExample1.docx");
// Get the first section of the document
Section section = doc.Sections[0];
// Get the first table in that section
Table table = (Table)section.Tables[0];
// Declare TableRow and TableCell variables for use within loops
TableRow tableRow;
TableCell tableCell;
// Iterate through all rows in the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.Rows.Count; i++)
{
// Get the current row
tableRow = table.Rows[i];
// Iterate through all cells in the current row
for (int j = 0; j < tableRow.Cells.Count; j++)
{
// Get the current cell
tableCell = tableRow.Cells[j];
// Set the border style of the current cell to single line
tableCell.CellFormat.Borders.BorderType = Spire.Doc.Documents.BorderStyle.Single;
}
}
// Save the modified document as a new file
doc.SaveToFile("AddBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Close the document to release resources
doc.Close();
}
}
}
C# Modify Word Table Borders
Spire.Doc offers a range of border properties such as the border style TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.BorderType, border width TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.LineWidth, and border color TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.Color, among others. You can customize these properties to achieve the desired effects. Below are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the first section of the document using Document.Sections[0].
- Get the first table in the section using Section.Tables[0].
- Use a for loop to iterate over the cells in the table whose border styles you wish to change.
- Change the bottom border color of the cell by setting TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.Bottom.Color to Color.PaleVioletRed.
- Change the bottom border style of the cell by setting TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.Bottom.BorderType to BorderStyle.DotDash.
- Change the bottom border width of the cell by setting TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.Bottom.LineWidth to 2 points.
- Save the changes to the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Drawing;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("TableExample2.docx");
// Get the first section of the document
Section section = doc.Sections[0];
// Get the first table in that section
Table table = (Table)section.Tables[0];
// Declare a TableRow to use within the loop
TableRow tableRow;
// Iterate through all rows of the table
for (int i = 1; i < table.Rows.Count - 1; i++)
{
tableRow = table.Rows[i];
// Set the border color of the current cell
tableRow.Cells[1].CellFormat.Borders.Bottom.Color = Color.PaleVioletRed;
// Set the border style of the current cell to DotDash
tableRow.Cells[1].CellFormat.Borders.Bottom.BorderType = Spire.Doc.Documents.BorderStyle.DotDash;
// Set the width of the border
tableRow.Cells[1].CellFormat.Borders.Bottom.LineWidth = 2;
}
// Save the modified document as a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Close the document and release resources
doc.Close();
}
}
}
C# Remove Word Table Borders
During the process of handling Word documents, not only can border styles be applied to entire tables, but customization can also be extended to individual cells. To completely remove all borders from a table, it is recommended to follow a two-step strategy: First, apply border removal settings to the table itself; second, visit each cell within the table individually to clear their border styles. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the first table in the section using Section.Tables[0].
- Use a for loop to iterate over all cells in the table.
- Set Table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.None to remove borders from the table.
- Set TableCell.CellFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.None to remove borders from each cell.
- Save the changes to the Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Drawing;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from file
doc.LoadFromFile("TableExample2.docx");
// Get the first section of the document
Section section = doc.Sections[0];
// Get the first table in that section
Table table = (Table)section.Tables[0];
// Remove the borders set on the table
table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.None;
// Declare a TableRow to use in the loop
TableRow tableRow;
// Iterate through all rows in the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.Rows.Count; i++)
{
tableRow = table.Rows[i];
for (int j = 0; j < tableRow.Cells.Count; j++)
{
// Remove all borders set on the cell
tableRow.Cells[j].CellFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.None;
}
}
// Save the modified document as a new file
doc.SaveToFile("RemoveBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Close the document to release resources
doc.Close();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Add, Modify, or Remove Word Table Borders
In Word documents, the ability to add, modify, and remove table borders flexibly can significantly enhance readability and professionalism. Firstly, customizing border styles highlights important information, helping readers quickly locate key data or paragraphs and enhancing visual impact. Secondly, by adjusting the thickness, color, and style of border lines, finer design control can be achieved, ensuring a uniform and aesthetically pleasing document style. Lastly, removing unnecessary borders helps reduce visual clutter, making page layouts cleaner and more comprehensible, improving the reading experience. This article will introduce how to add, modify, or remove Word table borders in Java projects using Spire.Doc for Java.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Java Add Word Table Borders
To uniformly add borders to all cells in a table, you need to visit each cell individually and visually set its border properties. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the first section of the document using Document.getSections().get(0).
- Get the first table within the section using Section.getTables().get(0).
- Use a for loop to iterate through all cells in the table.
- Set the cell border to a single line style by using TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.Single).
- Define the border width to 1 point by using TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().setLineWidth(1f).
- Set the border color to black by using TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().setColor(Color.black).
- Save the changes to the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class AddBorder {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from file
doc.loadFromFile("TableExample1.docx");
// Get the first section of the document
Section section = doc.getSections().get(0);
// Get the first table in the section
Table table = section.getTables().get(0);
// Declare TableRow and TableCell variables for use in the loop
TableRow tableRow;
TableCell tableCell;
// Iterate through all rows of the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.getRows().getCount(); i++) {
// Get the current row
tableRow = table.getRows().get(i);
// Iterate through all cells in the current row
for (int j = 0; j < tableRow.getCells().getCount(); j++) {
// Get the current cell
tableCell = tableRow.getCells().get(j);
// Set the border style of the current cell to single line
tableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.Single);
// Set the width of the border
tableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().setLineWidth(1f);
// Set the color of the border
tableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().setColor(Color.black);
}
}
// Save the modified document as a new file
doc.saveToFile("AddBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close the document to release resources
doc.close();
}
}
Java Modify Word Table Borders
Spire.Doc empowers users with extensive customization options for borders, allowing adjustments such as selecting border styles through TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom().setBorderType(), setting border thickness via TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom().setLineWidth(), and specifying border colors with TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom().setColor(). This enables fine-tuned design of table borders within documents according to personal or project needs. Below are the detailed steps:
- Instantiate a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the first section of the document by calling Document.getSections().get(0).
- Get the first table within the section using Section.getTables().get(0).
- Iterate over the cells in the table that require border style changes using a for loop.
- Change the color of the bottom border to orange by invoking TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom ().setColor(Color.ORANGE).
- Alter the style of the bottom border to a dashed line by calling TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom ().setBorderType(BorderStyle.Dot_Dash).
- Modify the width of the bottom border to 2 points by executing TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom ().setLineWidth(2).
- Save the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ModifyBorder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.loadFromFile("TableExample2.docx");
// Get the first section of the document
Section section = doc.getSections().get(0);
// Get the first table in that section
Table table = section.getTables().get(0);
// Declare a TableRow to use within the loop
TableRow tableRow;
// Iterate through all rows of the table
for (int i = 1; i < table.getRows().getCount() - 1; i++) {
tableRow = table.getRows().get(i);
// Set the border color of the current cell tableRow.getCells().get(1).getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom().setColor(Color.ORANGE);
// Set the border style of the current cell to dotted line
tableRow.getCells().get(1).getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom().setBorderType(BorderStyle.Dot_Dash);
// Set the width of the border
tableRow.getCells().get(1).getCellFormat().getBorders().getBottom().setLineWidth(2);
}
// Save the modified document as a new file
doc.saveToFile("ModifyBorder.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close the document to release resources
doc.close();
}
}
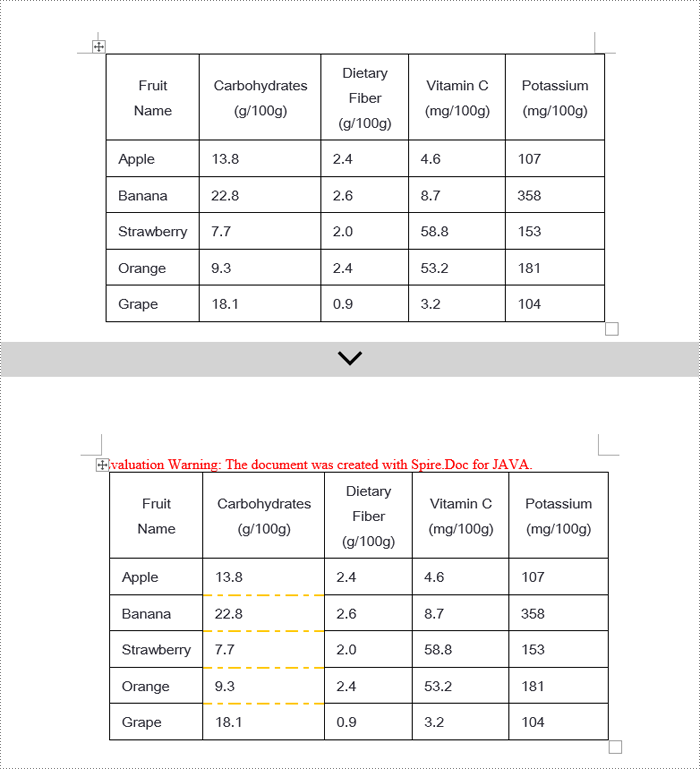
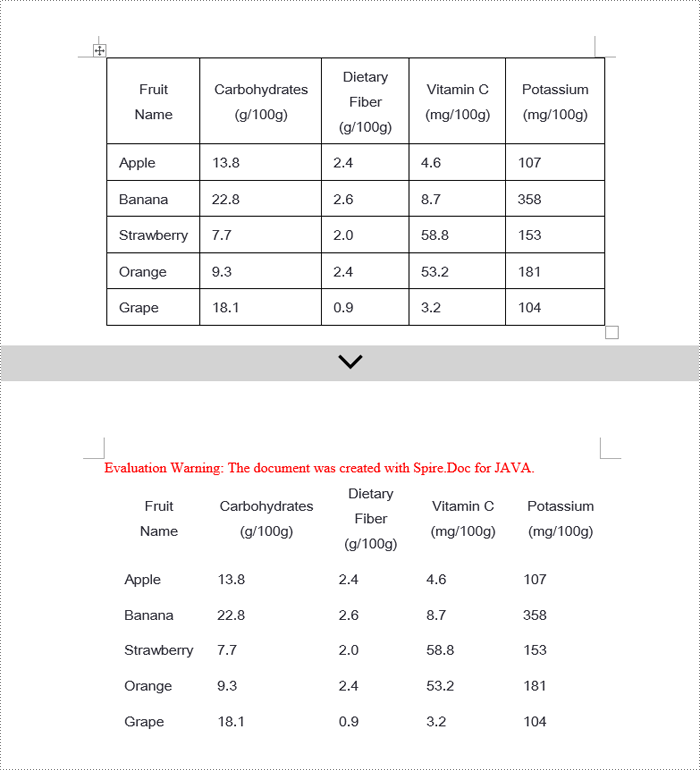
Java Remove Word Table Borders
When editing Word documents, the flexibility of border design extends beyond the entire table level, allowing for meticulous personalized adjustments at the individual cell level. To comprehensively remove all traces of borders both inside and outside of tables, a phased approach is recommended: Firstly, address the macro-level by clearing the overall border style of the table; subsequently, enter the micro-adjustment phase where each cell within the table is iterated over to revoke its unique border settings. Below are the detailed steps:
- Instantiate a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the first section of the document by calling Document.getSections().get(0).
- Access the first table within the section using Section.getTables().get(0).
- Iterate over all cells in the table using a for loop.
- Remove the border of the table by invoking Table.getTableFormat().getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.None).
- Eliminate the borders of each cell individually by applying TableCell.getCellFormat().getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.None).
- Save the modified document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.BorderStyle;
public class RemoveBorder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.loadFromFile("TableExample2.docx");
// Get the first section of the document
Section section = doc.getSections().get(0);
// Get the first table in the section
Table table = section.getTables().get(0);
// Remove the borders set on the table
table.getTableFormat().getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.None);
// Declare a TableRow to use in the loop
TableRow tableRow;
// Iterate through all rows of the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.getRows().getCount(); i++) {
tableRow = table.getRows().get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < tableRow.getCells().getCount(); j++) {
// Remove all borders set on the cell tableRow.getCells().get(j).getCellFormat().getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.None);
}
}
// Save the modified document as a new file
doc.saveToFile("RemoveBorder.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close the document and release resources
doc.close();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Copy Rows, Columns and Cells in Excel
Copying data in Excel is a fundamental feature that allows you to quickly and efficiently reproduce data. It can be especially valuable when building spreadsheets with similar structures, or needing to propagate the same information across multiple areas of your workbook. By mastering the art of copying in Excel, you can boost your productivity and reduce the risk of manual data entry errors. In this article, we will explain how to copy rows, columns and cells in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Copy Rows in Excel in Python
You can use the Worksheet.CopyRow(sourceRow, destSheet, destRowIndex, copyOptions) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python to easily copy a row in the same or between different worksheets in Excel. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired row that you want to copy using the Worksheet.Rows[index] property.
- Copy the row and its format from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.CopyRow(sourceRow, destSheet, destRowIndex, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the column widths of cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the desired row that you want to copy
row = sheet1.Rows[0]
# Copy the row from the source worksheet to the first row of the destination worksheet
sheet1.CopyRow(row, sheet2, 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
columns = sheet1.Columns.Length
# Copy the column widths of the cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row
for i in range(columns):
column_width = row.Columns[i].ColumnWidth
sheet2.Rows[0].Columns[i].ColumnWidth = column_width
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyRow.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
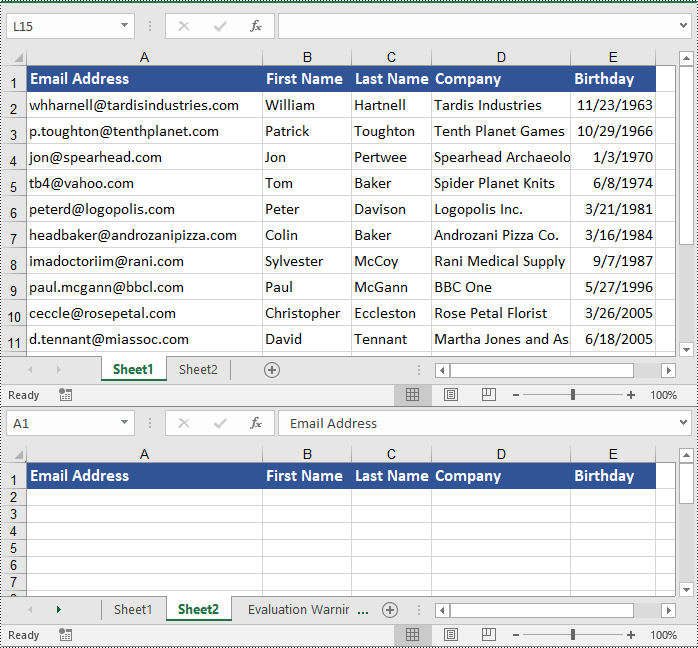
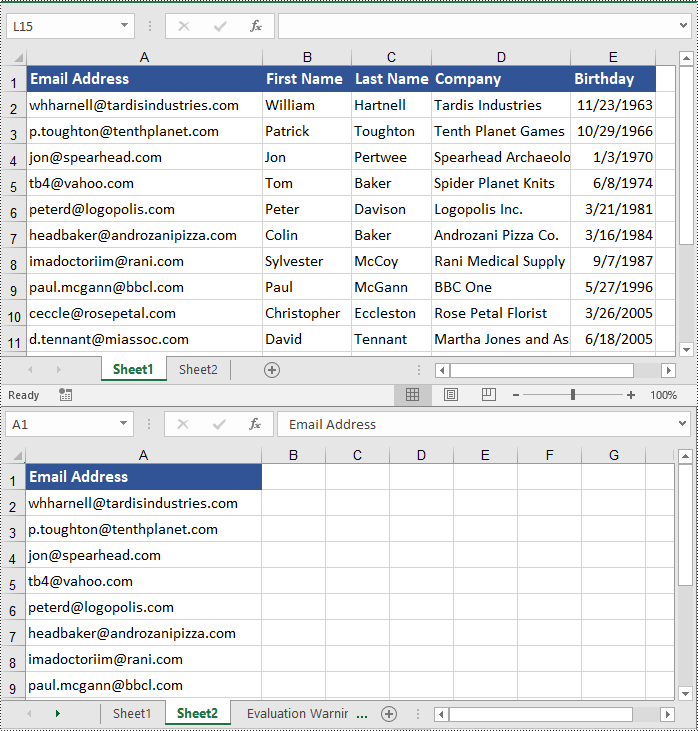
Copy Columns in Excel in Python
To copy a column in an Excel worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.CopyColumn(sourceColumn, destSheet, destColIndex, copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired column that you want to copy using the Worksheet.Columns[index] property.
- Copy the column and its format from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.CopyColumn(sourceColumn, destSheet, destColIndex, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the desired column that you want to copy
column = sheet1.Columns[0]
# Copy the column from the source worksheet to the first column of the destination worksheet
sheet1.CopyColumn(column, sheet2, 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
rows = column.Rows.Length
# Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column
for i in range(rows):
row_height = column.Rows[i].RowHeight
sheet2.Columns[0].Rows[i].RowHeight = row_height
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
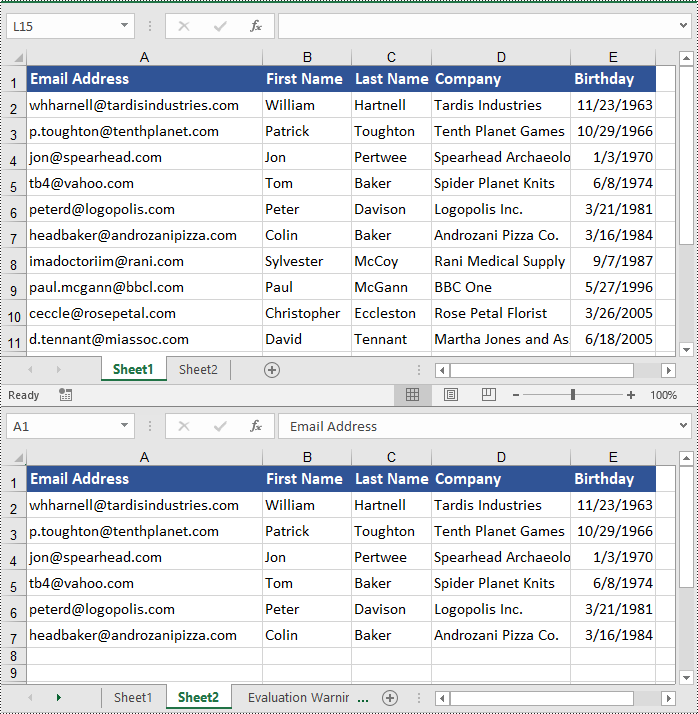
Copy Cells in Excel in Python
In addition to copying entire rows and columns, you are also able to copy an individual cell or a range of cells using the CellRange.Copy(destRange, copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the source cell range and the destination cell range using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Copy the source cell range and its format from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet using the CellRange.Copy(destRange, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the source cell range
range1 = sheet1.Range["A1:E7"]
# Get the destination cell range
range2 = sheet2.Range["A1:E7"]
# Copy the source cell range from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet
range1.Copy(range2, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range
for i, row in enumerate(range1.Rows):
for j, column in enumerate(row.Columns):
range2.Rows[i].Columns[j].ColumnWidth = column.ColumnWidth
range2.Rows[i].RowHeight = row.RowHeight
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Spire.Doc for Java 12.6.2 supports displaying a prompt message when a corresponding font is not found during conversion
We're pleased to announce the release of Spire.Doc for Java 12.6.2. This version supports displaying a prompt message when a corresponding font is not found during Word conversion. Meanwhile, it also fixes some issues that occurred when converting Word to PDF, and HTML to Word. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREDOC-10465 | Supports displaying a prompt message when a corresponding font is not found during Word conversion.
Document doc = ConvertUtil.GetNewEngineDocument();
doc.loadFromFile(input);
HandleDocumentSubstitutionWarnings substitutionWarningHandler = new HandleDocumentSubstitutionWarnings();
doc.setWarningCallback(substitutionWarningHandler);
doc.saveToFile(output_1);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Iterator iterator = substitutionWarningHandler.FontWarnings.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(((WarningInfo)iterator.next()).getDescription());
}
String s = substitutionWarningHandler.FontWarnings.get(0).getDescription();
WarningSource warningSource = substitutionWarningHandler.FontWarnings.get(0).getSource();
substitutionWarningHandler.FontWarnings.clear();
class HandleDocumentSubstitutionWarnings implements IWarningCallback
{
public void warning(WarningInfo info) {
if(info.getWarningType() == WarningType.Font_Substitution)
FontWarnings.warning(info);
}
public WarningInfoCollection FontWarnings = new WarningInfoCollection();
}
|
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10413 | Fixes the issue that the text shifted upwards when converting a Word document to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10486 | Fixes the issue that the content layout was inconsistent when converting a Word document to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10504 | Fixes the issue that the application threw a "'td' is expected" error when converting an HTML to Word. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10589 | Fixes the issue that text content was partially lost when converting a Word document to an image. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10592 | Fixes the issue that the application threw a "String index out of range: -1" error when converting a Word document to PDF |
Spire.XLS for Java 14.6.2 enhances the conversion from Excel to images
We are delighted to announce the release of Spire.XLS for Java 14.6.2. This version enhances the conversion from Excel to images. Besides, some known issues are fixed in this version, such as the issue that the effect of setting "autoFitColumns()" was incorrect. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5223 | Fixes the issue that the formula values were calculated incorrectly when transferring Excel to images. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5238 | Fixes the issue that the effect of setting "autoFitColumns()" was incorrect. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5256 | Fixes the issue that an exception "com.spire.xls.packages.spramg: Invalid cell name" was thrown when loading an Excel document. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5263 | Fixes the issue that annotations added by Microsoft 365 in Excel documents were lost after loading and saving. |