Excel is a powerful spreadsheet software with numerous features, but formulas and functions are undoubtedly among its most critical tools. They enable users to perform a wide range of mathematical, statistical, and logical operations on their data, allowing them to derive meaningful insights quickly and accurately. In this article, we will explain how to add or read formulas and functions in Excel files in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Add Formulas and Functions to Excel in C# and VB.NET
- Read Formulas and Functions in Excel in C# and VB.NET
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
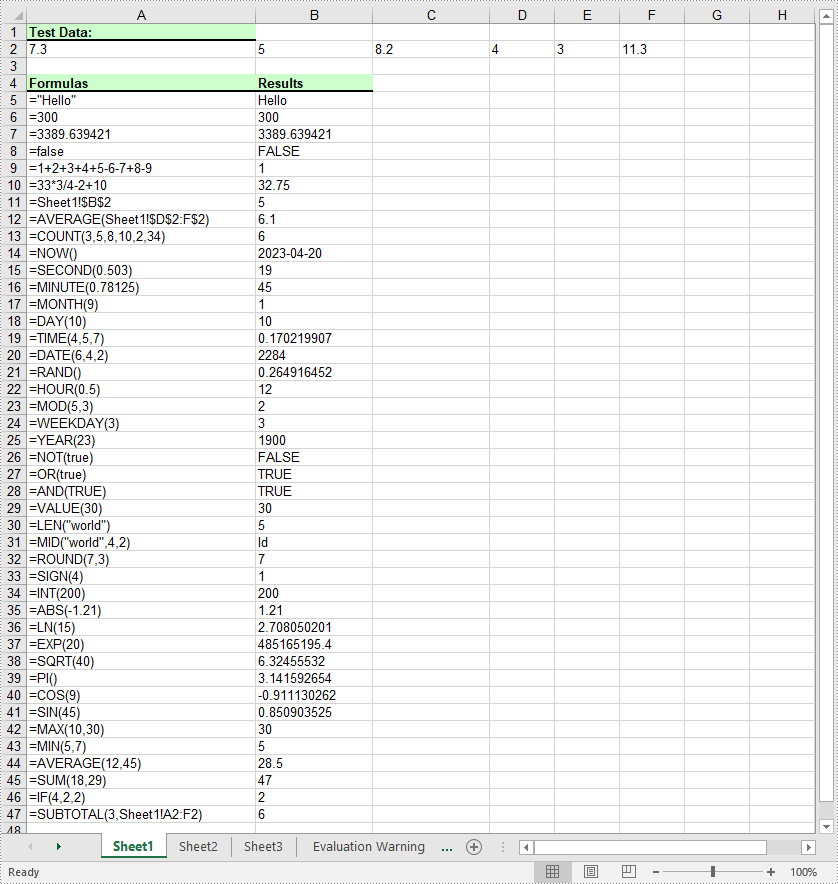
Add Formulas and Functions to Excel in C# and VB.NET
The Worksheet.Range[int row, int column].Formula property in Spire.XLS for .NET is used to add formulas or functions to specific cells in an Excel worksheet. The main steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Add some text and numeric data to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet.Range[int row, int column].Text and Worksheet.Range[int row, int column].NumberValue properties.
- Add text and formulas to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet.Range[int row, int column].Text and Worksheet.Range[int row, int column].Formula properties.
- Add text and functions to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet.Range[int row, int column].Text and Worksheet.Range[int row, int column].Formula properties.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile(string fileName, ExcelVersion version) method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace AddFormulasAndFunctions
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Declare two variables: currentRow, currentFormula
int currentRow = 1;
string currentFormula;
//Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "Test Data:";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Solid;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium;
//Add some numeric data to the worksheet
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].NumberValue = 7.3;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].NumberValue = 5;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 3].NumberValue = 8.2;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 4].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 5].NumberValue = 3;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 6].NumberValue = 11.3;
currentRow++;
//Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "Formulas";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Text = "Results";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Solid;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium;
//Add text and formulas to the worksheet
currentFormula = "=\"Hello\"";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
currentFormula = "=300";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
currentFormula = "=3389.639421";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
currentFormula = "=false";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
currentFormula = "=1+2+3+4+5-6-7+8-9";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
currentFormula = "=33*3/4-2+10";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
currentFormula = "=Sheet1!$B$2";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//Add text and Functions to the worksheet
//AVERAGE
currentFormula = "=AVERAGE(Sheet1!$D$2:F$2)";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//COUNT
currentFormula = "=COUNT(3,5,8,10,2,34)";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//NOW
currentFormula = "=NOW()";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Style.NumberFormat = "yyyy-MM-DD";
//SECOND
currentFormula = "=SECOND(0.503)";
sheet.Range[++currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//MINUTE
currentFormula = "=MINUTE(0.78125)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//MONTH
currentFormula = "=MONTH(9)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//DAY
currentFormula = "=DAY(10)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//TIME
currentFormula = "=TIME(4,5,7)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//DATE
currentFormula = "=DATE(6,4,2)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//RAND
currentFormula = "=RAND()";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//HOUR
currentFormula = "=HOUR(0.5)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//MOD
currentFormula = "=MOD(5,3)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//WEEKDAY
currentFormula = "=WEEKDAY(3)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//YEAR
currentFormula = "=YEAR(23)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//NOT
currentFormula = "=NOT(true)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//OR
currentFormula = "=OR(true)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//AND
currentFormula = "=AND(TRUE)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//VALUE
currentFormula = "=VALUE(30)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//LEN
currentFormula = "=LEN(\"world\")";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//MID
currentFormula = "=MID(\"world\",4,2)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//ROUND
currentFormula = "=ROUND(7,3)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//SIGN
currentFormula = "=SIGN(4)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//INT
currentFormula = "=INT(200)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//ABS
currentFormula = "=ABS(-1.21)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//LN
currentFormula = "=LN(15)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//EXP
currentFormula = "=EXP(20)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//SQRT
currentFormula = "=SQRT(40)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//PI
currentFormula = "=PI()";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//COS
currentFormula = "=COS(9)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//SIN
currentFormula = "=SIN(45)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//MAX
currentFormula = "=MAX(10,30)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//MIN
currentFormula = "=MIN(5,7)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//AVERAGE
currentFormula = "=AVERAGE(12,45)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//SUM
currentFormula = "=SUM(18,29)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//IF
currentFormula = "=IF(4,2,2)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//SUBTOTAL
currentFormula = "=SUBTOTAL(3,Sheet1!A2:F2)";
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula;
sheet.Range[currentRow++, 2].Formula = currentFormula;
//Set width of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd columns
sheet.SetColumnWidth(1, 32);
sheet.SetColumnWidth(2, 16);
sheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 16);
//Create a cell style
CellStyle style = workbook.Styles.Add("Style");
//Set the horizontal alignment as left
style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
//Apply the style to the worksheet
sheet.ApplyStyle(style);
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddFormulasAndFunctions.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
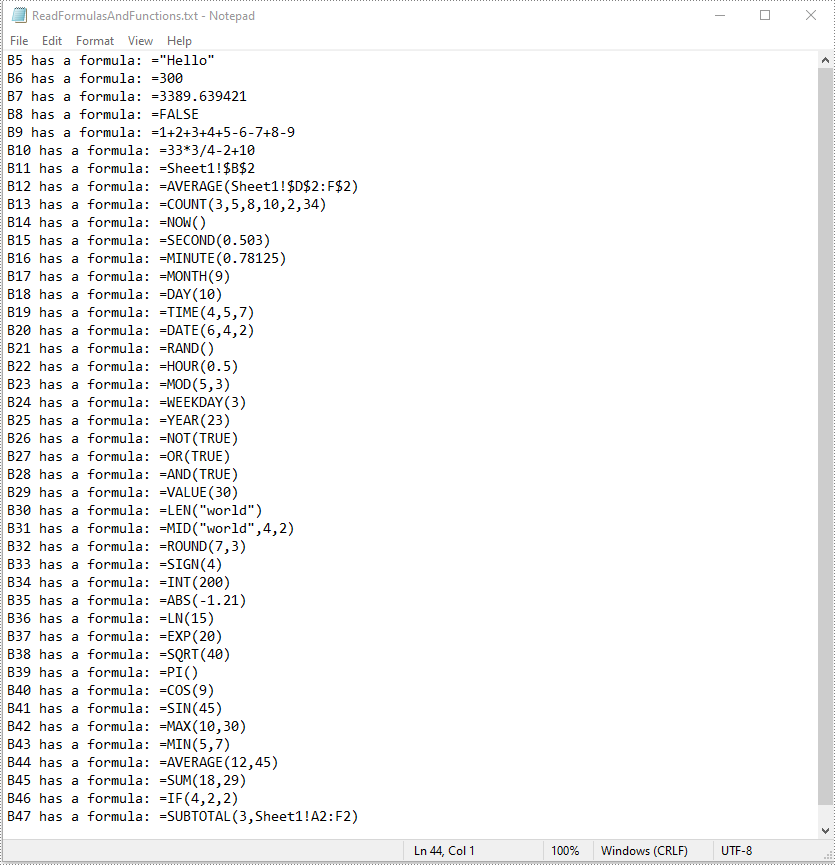
Read Formulas and Functions in Excel in C# and VB.NET
To read formulas and functions in an Excel worksheet, you need to iterate through all the cells in the worksheet, after that, find the cells containing formulas or functions using the Cell.HasFormula property, then get the formulas or functions of the cells using the CellRange.Formula property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Initialize an instance of the StringBuilder class.
- Access the used range of the worksheet using the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Iterate through all the cells in the used range.
- Find the cells containing formulas/functions using the Cell.HasFormula property.
- Get the names and the formulas/functions of the cells using the CellRange.RangeAddressLocal and CellRange.Formula properties.
- Append the cell names and formulas/functions to the StringBuilder using the StringBuilder.AppendLine() method.
- Write the content of the StringBuilder into a .txt file using the File.WriteAllText() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
namespace ReadFormulasAndFunctions
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddFormulasAndFunctions.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Initialize an instance of the StringBuilder class
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//Access the used range of the worksheet
CellRange usedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange;
//Loop through all the cells in the used range
foreach (CellRange cell in usedRange)
{
//Detect if the current cell has formula/function
if (cell.HasFormula)
{
//Get the cell name
string cellName = cell.RangeAddressLocal;
//Get the formula/function
string formula = cell.Formula;
//Append the cell name and formula/function to the StringBuilder
sb.AppendLine(cellName + " has a formula: " + formula);
}
}
//Write the content of the StringBuilder into a .txt file
File.WriteAllText("ReadFormulasAndFunctions.txt", sb.ToString());
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.


