C#: Count Words, Characters, Paragraphs, Lines, and Pages in Word Documents
Accurate counting of words, characters, paragraphs, lines, and pages is essential in achieving precise document analysis. By meticulously tracking these metrics, writers can gain valuable insights into the length, structure, and overall composition of their work. In this article, we will explain how to count words, characters, paragraphs, lines, and pages in Word documents in C# using Spire.Doc for .NET.
- Count Words, Characters, Paragraphs, Lines, and Pages in a Word Document in C#
- Count Words and Characters in a Specific Paragraph of a Word Document in C#
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
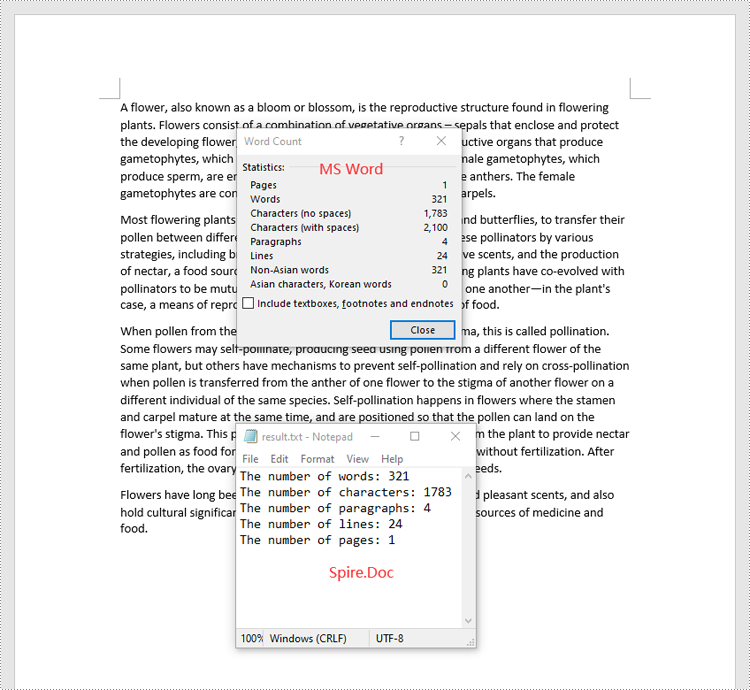
Count Words, Characters, Paragraphs, Lines, and Pages in a Word Document in C#
Spire.Doc for .NET provides the BuiltinDocumentProperties class that enables you to retrieve crucial information from your Word documents. By using this class, you can access a wealth of details, including both the built-in and custom properties, as well as the precise counts of words, characters, paragraphs, lines, and pages contained within the document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an object of the Document class.
- Load a sample Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the BuiltinDocumentProperties object using the Document.BuiltinDocumentProperties property.
- Get the numbers of words, characters, paragraphs, lines, and pages in the document using the WordCount, CharCount, ParagraphCount, LinesCount and PageCount properties of the BuiltinDocumentProperties class.
- Initialize an object of the StringBuilder class and append the results to it using the StringBuilder.AppendLine() method.
- Write the content in the StringBuilder to a text file using the File.WriteAllText() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
namespace CountWordsCharactersEtcInWord
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Initialize an object of the Document class
Document document = new Document();
//Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Input.docx");
//Get the BuiltinDocumentProperties object
BuiltinDocumentProperties properties = document.BuiltinDocumentProperties;
//Get the numbers of words, characters, paragraphs, lines, and pages in the document
int wordCount = properties.WordCount;
int charCount = properties.CharCount;
int paraCount = properties.ParagraphCount;
int lineCount = properties.LinesCount;
int pageCount = properties.PageCount;
//Initialize an object of the StringBuilder class
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//Append the results to the StringBuilder
sb.AppendLine("The number of words: " + wordCount);
sb.AppendLine("The number of characters: " + charCount);
sb.AppendLine("The number of paragraphs: " + paraCount);
sb.AppendLine("The number of lines: " + lineCount);
sb.AppendLine("The number of pages: " + pageCount);
//Write the content of the StringBuilder to a text file
File.WriteAllText("result.txt", sb.ToString());
document.Close();
}
}
}
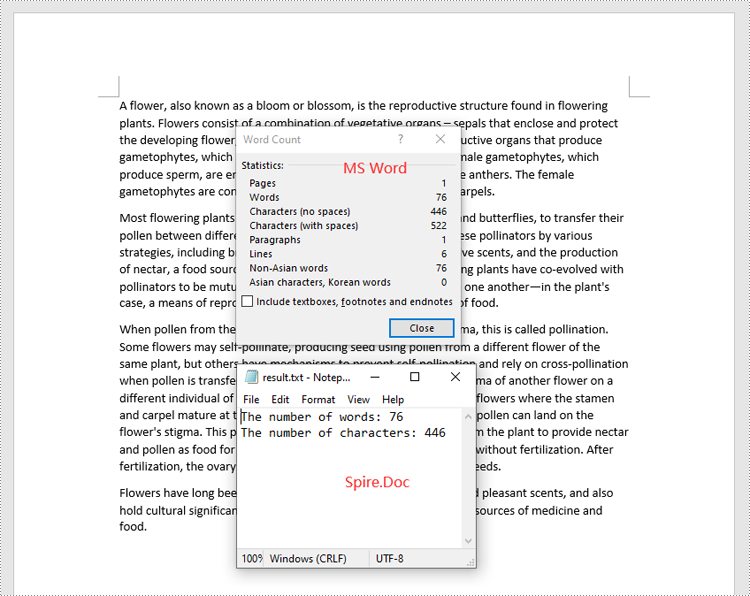
Count Words and Characters in a Specific Paragraph of a Word Document in C#
In addition to counting the words and characters in an entire Word document, Spire.Doc for .NET enables you to count the words and characters of a specific paragraph by using the Paragraph.WordCount and Paragraph.CharCount properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an object of the Document class.
- Load a sample Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific paragraph using the Document.Sections[sectionindex].Paragraphs[paragraphIndex] property.
- Get the numbers of words and characters in the paragraph using the Paragraph.WordCount and Paragraph.CharCount properties.
- Initialize an object of the StringBuilder class and append the results to it using the StringBuilder.AppendLine() method.
- Write the content in the StringBuilder to a text file using the File.WriteAllText() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
namespace CountWordsAndCharactersForParagraph
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Initialize an object of the Document class
Document document = new Document();
//Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Input.docx");
//Get a specific paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = document.Sections[0].Paragraphs[0];
//Get the numbers of words and characters in the paragraph
int wordCount = paragraph.WordCount;
int charCount = paragraph.CharCount;
//Initialize an object of the StringBuilder class
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//Append the results to the StringBuilder
sb.AppendLine("The number of words: " + wordCount);
sb.AppendLine("The number of characters: " + charCount);
//Write the content of the StringBuilder to a text file
File.WriteAllText("result.txt", sb.ToString());
document.Close();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#: Modify Content Controls in a Word Document
In a Word document, content controls allow the content of the document to be dynamically updated and modified, providing users with more flexible editing and management options. Through content controls, users can easily insert, delete, or modify content in specific sections without altering the overall structure of the document. This article will explain how to use Spire.Doc for .NET to modify content controls in a Word document within a C# project.
- Modify Content Controls in the Body using C#
- Modify Content Controls within Paragraphs using C#
- Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Rows using C#
- Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Cells using C#
- Modify Content Controls within Table Cells using C#
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
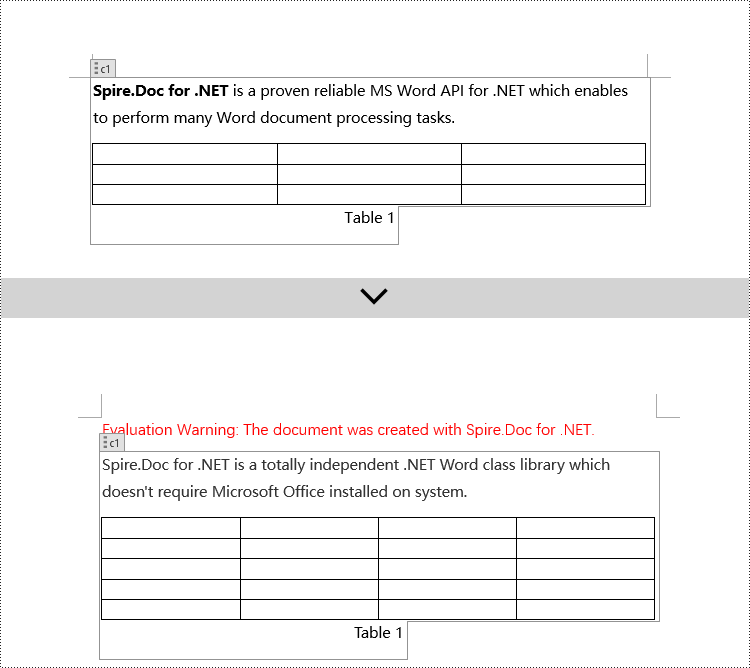
Modify Content Controls in the Body using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for content controls in the body is StructureDocumentTag. You can iterate through the collection of child objects in Section.Body to find objects of type StructureDocumentTag and then modify them. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the body of a section in the document using Section.Body.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the body, Body.ChildObjects, to find objects of type StructureDocumentTag.
- Access the StructureDocumentTag.ChildObjects collection and perform the necessary modification operations based on the type of child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Create lists for paragraphs and tables
List<Paragraph> paragraphs = new List<Paragraph>();
List<Table> tables = new List<Table>();
for (int i = 0; i < body.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Get the document object
DocumentObject documentObject = body.ChildObjects[i];
// If it is a StructureDocumentTag object
if (documentObject.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTag)
{
StructureDocumentTag structureDocumentTag = (StructureDocumentTag)documentObject;
// If the tag is "c1" or the alias is "c1"
if (structureDocumentTag.SDTProperties.Tag == "c1" || structureDocumentTag.SDTProperties.Alias == "c1")
{
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// If it is a paragraph object
if (structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph)
{
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph)structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j];
paragraphs.Add(paragraph);
}
// If it is a table object
if (structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Table)
{
Table table = (Table)structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j];
tables.Add(table);
}
}
}
}
}
// Modify the text content of the first paragraph
paragraphs[0].Text = "Spire.Doc for .NET is a totally independent .NET Word class library which doesn't require Microsoft Office installed on system.";
// Reset the cells of the first table
tables[0].ResetCells(5, 4);
// Save the modified document to a file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifyBodyContentControls.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Release document resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
Modify Content Controls within Paragraphs using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for content controls within paragraphs is StructureDocumentTagInline. To modify them, you need to iterate through the collection of child objects of Paragraph.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline, and then make the necessary modifications. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the body of a section in the document using Section.Body.
- Get the first paragraph of the body using Body.Paragraphs[0].
- Iterate through the collection of child objects of the paragraph, Paragraph.ChildObjects, to find objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline.
- Access the collection of child objects of StructureDocumentTagInline, StructureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects, and perform the required modifications based on the type of the child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first paragraph in the body
Paragraph paragraph = body.Paragraphs[0];
// Iterate through child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the child object is StructureDocumentTagInline
if (paragraph.ChildObjects[i].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagInline)
{
// Convert the child object to StructureDocumentTagInline type
StructureDocumentTagInline structureDocumentTagInline = (StructureDocumentTagInline)paragraph.ChildObjects[i];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property is "text1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Tag == "text1" || structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Alias == "text1")
{
// Iterate through child objects in the StructureDocumentTagInline object
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is a TextRange object
if (structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.TextRange)
{
// Convert the child object to TextRange type
TextRange range = (TextRange)structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j];
// Set the text content to a specified content
range.Text = "97-2003/2007/2010/2013/2016/2019";
}
}
}
// Check if the Tag or Alias property is "logo1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Tag == "logo1" || structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Alias == "logo1")
{
// Iterate through child objects in the StructureDocumentTagInline object
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is an image
if (structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture)
{
// Convert the child object to DocPicture type
DocPicture docPicture = (DocPicture)structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j];
// Load a specified image
docPicture.LoadImage("Doc-NET.png");
// Set the width and height of the image
docPicture.Width = 100;
docPicture.Height = 100;
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedContentControlsInParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Release resources of the Document object
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}

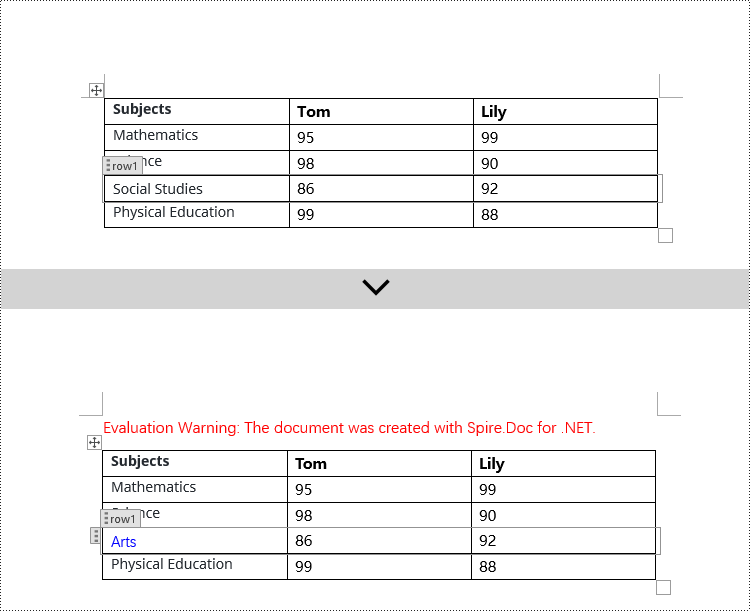
Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Rows using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for a table row content control is StructureDocumentTagRow. To modify it, you need to iterate through the child objects collection of Table.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagRow, and then make the necessary modifications. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the body of a section using Section.Body.
- Get the first table in the body using Body.Tables[0].
- Iterate through the child objects collection of the table, Table.ChildObjects, to find objects of type StructureDocumentTagRow.
- Access the collection of cells in the StructureDocumentTagRow.Cells table row content control and make the required modifications to the cell contents.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample3.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first table
Table table = (Table)body.Tables[0];
// Iterate through the child objects in the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the child object is of type StructureDocumentTagRow
if (table.ChildObjects[i].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagRow)
{
// Convert the child object to a StructureDocumentTagRow object
StructureDocumentTagRow structureDocumentTagRow = (StructureDocumentTagRow)table.ChildObjects[i];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of the StructureDocumentTagRow is "row1"
if (structureDocumentTagRow.SDTProperties.Tag == "row1" || structureDocumentTagRow.SDTProperties.Alias == "row1")
{
// Clear the paragraphs in the cell
structureDocumentTagRow.Cells[0].Paragraphs.Clear();
// Add a paragraph in the cell and set the text
TextRange textRange = structureDocumentTagRow.Cells[0].AddParagraph().AppendText("Arts");
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue;
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedTableRowContentControl.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Release document resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Cells using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for the content control in a table cell is StructureDocumentTagCell. You need to iterate through the collection of child objects in TableRow.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagCell, and then perform operations on them. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section using Section.Body.
- Get the first table in the body using Body.Tables[0].
- Iterate through the collection of table rows Table.Rows, accessing each TableRow object.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the table row TableRow.ChildObjects, finding objects of type StructureDocumentTagCell.
- Access the collection of paragraphs in the StructureDocumentTagCell content control cell, and perform the necessary modifications to the content.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample4.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first table in the document
Table table = (Table)body.Tables[0];
// Iterate through the rows of the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.Rows.Count; i++)
{
// Iterate through the child objects in each row
for (int j = 0; j < table.Rows[i].ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is a StructureDocumentTagCell
if (table.Rows[i].ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagCell)
{
// Convert the child object to StructureDocumentTagCell type
StructureDocumentTagCell structureDocumentTagCell = (StructureDocumentTagCell)table.Rows[i].ChildObjects[j];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of structureDocumentTagCell is "cell1"
if (structureDocumentTagCell.SDTProperties.Tag == "cell1" || structureDocumentTagCell.SDTProperties.Alias == "cell1")
{
// Clear the paragraphs in the cell
structureDocumentTagCell.Paragraphs.Clear();
// Add a new paragraph and add text to it
TextRange textRange = structureDocumentTagCell.AddParagraph().AppendText("92");
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue;
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedTableCellContentControl.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Dispose of the document object
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
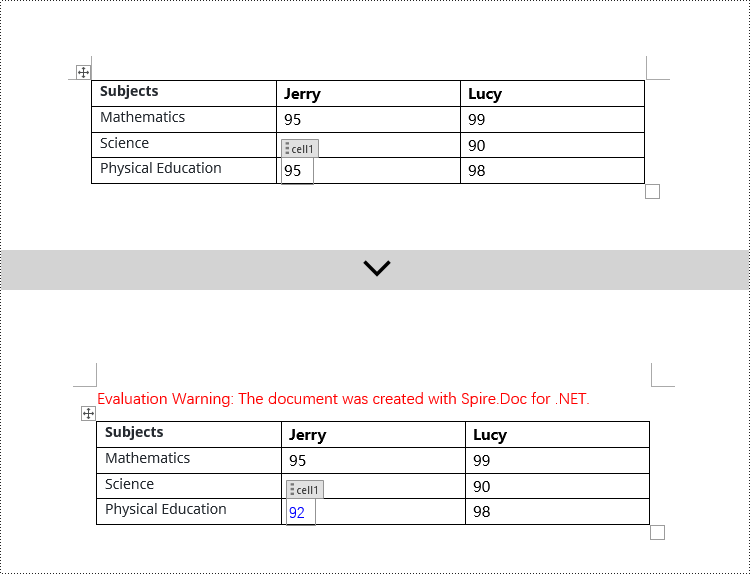
Modify Content Controls within Table Cells using C#
This case demonstrates modifying content controls within paragraphs in table cells. You need to first access the collection of paragraphs in the cell TableCell.Paragraphs, then iterate through the collection of child objects in each paragraph Paragraph.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline, and make modifications to them. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section using Section.Body.
- Get the first table in the body using Body.Tables[0].
- Iterate through the collection of table rows Table.Rows, accessing each TableRow object.
- Iterate through the collection of cells in the table row TableRow.Cells, accessing each TableCell object.
- Iterate through the collection of paragraphs in the cell TableCell.Paragraphs, accessing each Paragraph object.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the paragraph Paragraph.ChildObjects, finding objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline.
- Access the ChildObjects collection of the StructureDocumentTagInline object, and perform the necessary modifications based on the type of the child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample5.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first table
Table table = (Table)body.Tables[0];
// Iterate through the rows of the table
for (int r = 0; r < table.Rows.Count; r++)
{
// Iterate through the cells in the table row
for (int c = 0; c < table.Rows[r].Cells.Count; c++)
{
// Iterate through the paragraphs in the cell
for (int p = 0; p < table.Rows[r].Cells[c].Paragraphs.Count; p++)
{
// Get the paragraph object
Paragraph paragraph = table.Rows[r].Cells[c].Paragraphs[p];
// Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the child object is of type StructureDocumentTagInline
if (paragraph.ChildObjects[i].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagInline)
{
// Convert to StructureDocumentTagInline object
StructureDocumentTagInline structureDocumentTagInline = (StructureDocumentTagInline)paragraph.ChildObjects[i];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of StructureDocumentTagInline is "test1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Tag == "test1" || structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Alias == "test1")
{
// Iterate through the child objects of StructureDocumentTagInline
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is of type TextRange
if (structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.TextRange)
{
// Convert to TextRange object
TextRange textRange = (TextRange)structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j];
// Set the text content
textRange.Text = "89";
// Set text color
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedContentControlInParagraphOfTableCell.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Dispose of the Document object resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
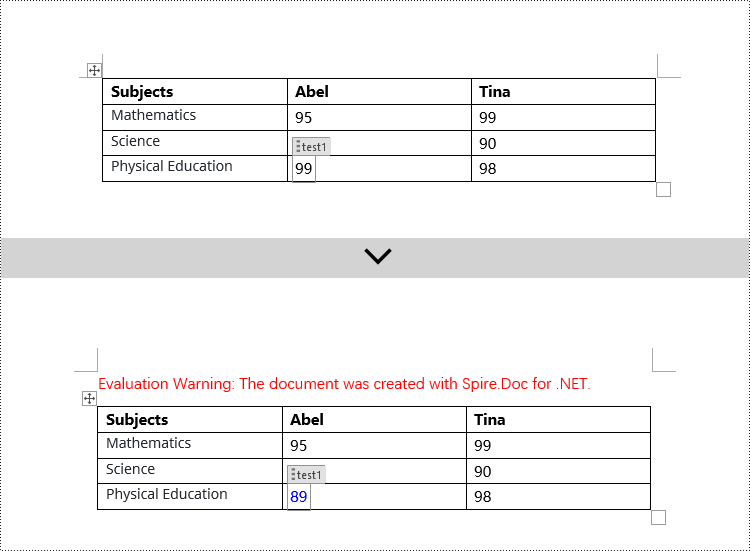
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
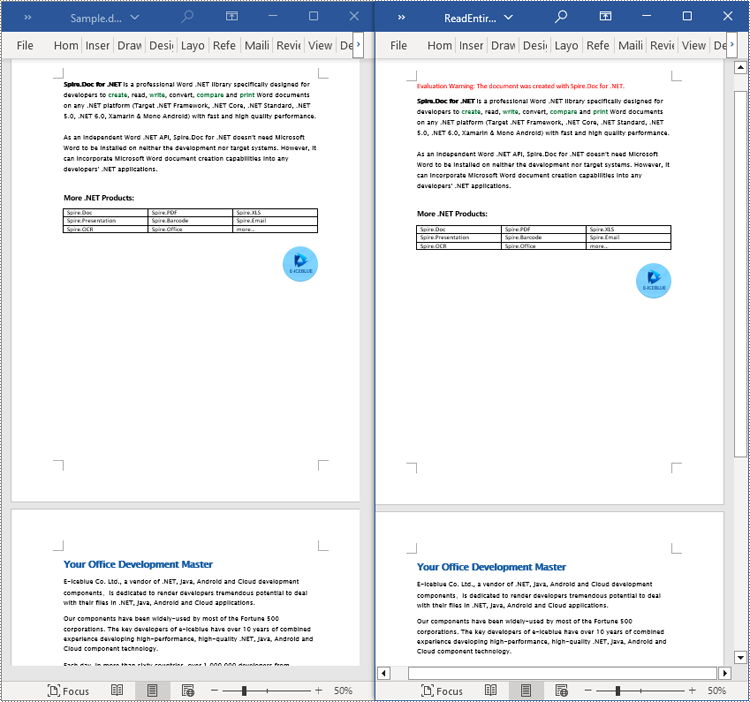
C# Read Content from a Word Document
Reading content from a Word document is crucial for many work and study tasks. Reading a page from a Word document helps in quickly browsing and summarizing key information, reading a section from a Word document aids in gaining a deeper understanding of a specific topic or section, while reading the entire document from a Word document allows for a comprehensive grasp of the overall information, facilitating comprehensive analysis and understanding. This article will introduce how to use Spire.Doc for .NET to read a page, a section, and the entire content of a Word document in a C# project.
- Read a Page from a Word Document in C#
- Read a Section from a Word Document in C#
- Reading the Entire Content from a Word Document in C#
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
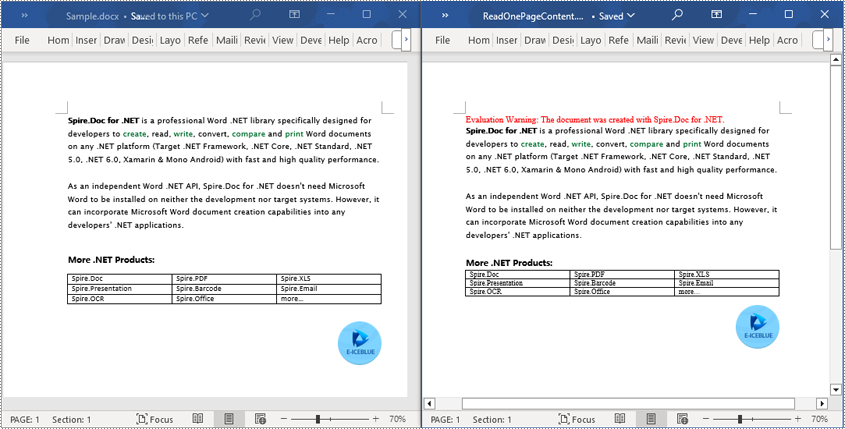
Read a Page from a Word Document in C#
By using the FixedLayoutDocument class and FixedLayoutPage class, you can easily retrieve the content of a specified page. To facilitate viewing the extracted content, this sample code will store the read content in a new Word document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Retrieve the FixedLayoutPage object of a page in the document.
- Access the Section where the page is located through the FixedLayoutPage.Section property.
- Get the index position of the first paragraph on the page within the section.
- Get the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Create another Document object.
- Add a new section using Document.AddSection().
- Clone the properties of the original section to the new section using the Section.CloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection) method.
- Copy the content of the page from the original document to the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Pages;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load document content from the specified file
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the first page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.Pages[0];
// Get the section where the page is located
Section section = page.Section;
// Get the first paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphStart = page.Columns[0].Lines[0].Paragraph;
int startIndex = 0;
if (paragraphStart != null)
{
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
startIndex = section.Body.ChildObjects.IndexOf(paragraphStart);
}
// Get the last paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.Columns[0].Lines[page.Columns[0].Lines.Count - 1].Paragraph;
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null)
{
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
endIndex = section.Body.ChildObjects.IndexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Add a new section
Section newSection = newdoc.AddSection();
// Clone the properties of the original section to the new section
section.CloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection);
// Copy the content of the page from the original document to the new document
for (int i = startIndex; i <= endIndex ; i++)
{
newSection.Body.ChildObjects.Add(section.Body.ChildObjects[i].Clone());
}
// Save the new document to a specified file
newdoc.SaveToFile("ReadOnePageContent.docx", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document
newdoc.Close();
newdoc.Dispose();
// Close and release the original document
document.Close();
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
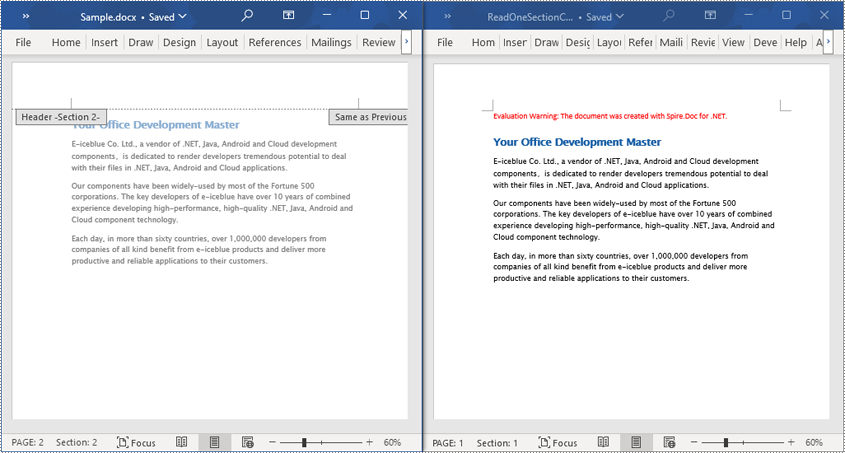
Read a Section from a Word Document in C#
By using Document.Sections[index], you can retrieve a specific Section object that contains the header, footer, and body content. This example provides a simple way to copy all content of a section to another document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Use the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load a Word document.
- Use Document.Sections[1] to retrieve the second section of the document.
- Create another new Document object.
- Use the Document.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method to clone the default style of the original document to the new document.
- Use newdoc.Sections.Add(section.Clone()) to clone the content of the second section of the original document into the new document.
- Use the Document.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting document.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the second section of the document
Section section = document.Sections[1];
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Clone the second section to the new document
newdoc.Sections.Add(section.Clone());
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.SaveToFile("ReadOneSectionContent.docx", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.Close();
newdoc.Dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.Close();
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
Read the Entire Content from a Word Document in C#
This example demonstrates reading the entire content of a document by iterating through each section of the original document and cloning each section into a new document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Use the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load a Word document.
- Create another new Document object.
- Use the Document.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method to clone the default style of the original document to the new document.
- Iterate through each section of the original document using a foreach loop and clone each section into the new document.
- Use the Document.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting document.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Iterate through each section in the original document and clone it to the new document
foreach (Section sourceSection in document.Sections)
{
newdoc.Sections.Add(sourceSection.Clone());
}
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.SaveToFile("ReadEntireDocumentContent.docx", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.Close();
newdoc.Dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.Close();
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#: Add, Insert, or Delete Pgaes in Word Documents
Adding, inserting, and deleting pages in a Word document is crucial for managing and presenting content. By adding or inserting a new page in Word, you can expand the document to accommodate more content, making it more structured and readable. Deleting pages can help streamline the document by removing unnecessary information or erroneous content. This article will explain how to use Spire.Doc for .NET to add, insert, or delete a page in a Word document within a C# project.
- Add a Page in a Word Document using C#
- Insert a Page in a Word Document using C#
- Delete a Page from a Word Document using C#
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Add a Page in a Word Document using C#
The steps to add a new page at the end of a Word document involve first obtaining the last section, then inserting a page break at the end of the last paragraph of that section to ensure that subsequently added content appears on a new page. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of the last section of the document using Document.LastSection.Body.
- Add a page break by calling Paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.PageBreak) method.
- Create a new ParagraphStyle object.
- Add the new paragraph style to the document's style collection using Document.Styles.Add() method.
- Create a new Paragraph object and set the text content.
- Apply the previously created paragraph style to the new paragraph using Paragraph.ApplyStyle(ParagraphStyle.Name) method.
- Add the new paragraph to the document using Body.ChildObjects.Add(Paragraph) method.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the body of the last section of the document
Body body = document.LastSection.Body;
// Insert a page break after the last paragraph in the body
body.LastParagraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.PageBreak);
// Create a new paragraph style
ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle = new ParagraphStyle(document);
paragraphStyle.Name = "CustomParagraphStyle1";
paragraphStyle.ParagraphFormat.LineSpacing = 12;
paragraphStyle.ParagraphFormat.AfterSpacing = 8;
paragraphStyle.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei";
paragraphStyle.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12;
// Add the paragraph style to the document's style collection
document.Styles.Add(paragraphStyle);
// Create a new paragraph and set the text content
Paragraph paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.AppendText("Thank you for using our Spire.Doc for .NET product. The trial version will add a red watermark to the generated document and only supports converting the first 10 pages to other formats. Upon purchasing and applying a license, these watermarks will be removed, and the functionality restrictions will be lifted.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.ApplyStyle(paragraphStyle.Name);
// Add the paragraph to the body's content collection
body.ChildObjects.Add(paragraph);
// Create another new paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.AppendText("To experience our product more fully, we provide a one-month temporary license free of charge to each of our customers. Please send an email to sales@e-iceblue.com, and we will send the license to you within one working day.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.ApplyStyle(paragraphStyle.Name);
// Add the paragraph to the body's content collection
body.ChildObjects.Add(paragraph);
// Save the document to the specified path
document.SaveToFile("Add a Page.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close the document
document.Close();
// Release the resources of the document object
document.Dispose();
Insert a Page in a Word Document using C#
Before inserting a new page, it is necessary to determine the ending position index of the specified page content within the section. Subsequently, add the content of the new page to the document one by one after this position. Finally, to separate the content from the following pages, adding a page break is essential. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Obtain the FixedLayoutPage object of a page in the document.
- Determine the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Create a new ParagraphStyle object.
- Add the new paragraph style to the document's style collection using Document.Styles.Add() method.
- Create a new Paragraph object and set the text content.
- Apply the previously created paragraph style to the new paragraph using the Paragraph.ApplyStyle(ParagraphStyle.Name) method.
- Insert the new paragraph at the specified using the Body.ChildObjects.Insert(index, Paragraph) method.
- Create another new paragraph object, set its text content, add a page break by calling the Paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.PageBreak) method, apply the previously created paragraph style, and then insert this paragraph into the document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Pages;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the sample document from a file
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the first page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.Pages[0];
// Get the body of the document
Body body = page.Section.Body;
// Get the last paragraph of the current page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.Columns[0].Lines[page.Columns[0].Lines.Count - 1].Paragraph;
// Initialize the end index
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null)
{
// Get the index of the last paragraph
endIndex = body.ChildObjects.IndexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Create a new paragraph style
ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle = new ParagraphStyle(document);
paragraphStyle.Name = "CustomParagraphStyle1";
paragraphStyle.ParagraphFormat.LineSpacing = 12;
paragraphStyle.ParagraphFormat.AfterSpacing = 8;
paragraphStyle.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei";
paragraphStyle.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12;
// Add the paragraph style to the document's style collection
document.Styles.Add(paragraphStyle);
// Create a new paragraph and set the text content
Paragraph paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.AppendText("Thank you for using our Spire.Doc for .NET product. The trial version will add a red watermark to the generated document and only supports converting the first 10 pages to other formats. Upon purchasing and applying a license, these watermarks will be removed, and the functionality restrictions will be lifted.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.ApplyStyle(paragraphStyle.Name);
// Insert the paragraph at the specified position
body.ChildObjects.Insert(endIndex + 1, paragraph);
// Create another new paragraph
paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.AppendText("To experience our product more fully, we provide a one-month temporary license free of charge to each of our customers. Please send an email to sales@e-iceblue.com, and we will send the license to you within one working day.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.ApplyStyle(paragraphStyle.Name);
// Add a page break
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.PageBreak);
// Insert the paragraph at the specified position
body.ChildObjects.Insert(endIndex + 2, paragraph);
// Save the document to the specified path
document.SaveToFile("Insert a Page.docx", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the original document
document.Close();
document.Dispose();
}
}
}

Delete a Page from a Word Document using C#
To delete the content of a page, first determine the index positions of the starting and ending elements of that page in the document. Then, you can utilize a loop to systematically remove these elements one by one. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Obtain the FixedLayoutPage object of the first page in the document.
- Use the FixedLayoutPage.Section property to get the section where the page is located.
- Determine the index position of the first paragraph on the page within the section.
- Determine the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Use a for loop to remove the content of the page one by one.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Pages;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the sample document from a file
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the second page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.Pages[1];
// Get the section of the page
Section section = page.Section;
// Get the first paragraph on the first page
Paragraph paragraphStart = page.Columns[0].Lines[0].Paragraph;
int startIndex = 0;
if (paragraphStart != null)
{
// Get the index of the starting paragraph
startIndex = section.Body.ChildObjects.IndexOf(paragraphStart);
}
// Get the last paragraph on the last page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.Columns[0].Lines[page.Columns[0].Lines.Count - 1].Paragraph;
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null)
{
// Get the index of the ending paragraph
endIndex = section.Body.ChildObjects.IndexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Delete all content within the specified range
for (int i = 0; i <= (endIndex - startIndex); i++)
{
section.Body.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(startIndex);
}
// Save the document to the specified path
document.SaveToFile("Delete a Page.docx", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the original document
document.Close();
document.Dispose();
}
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Insert Lists in a Word Document
Lists are used in Word documents to outline, arrange, and emphasize text, making it easy for users to scan and understand a series of items. There are three different types of lists in Word, namely numbered lists, bulleted lists and multi-level lists. Numbered lists are used for items that have a sequence or priority, such as a series of instructions. Bulleted lists are used for items that have no particular priority, such as a list of functions or facts. Multi-level lists are used where there is a sequence and you want each paragraph numbered separately.
In this article, you will learn how to insert these types of lists into a Word document in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Doc for .NET.
- Insert a Numbered List in Word
- Insert a Bulleted List in Word
- Insert a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word
- Insert a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
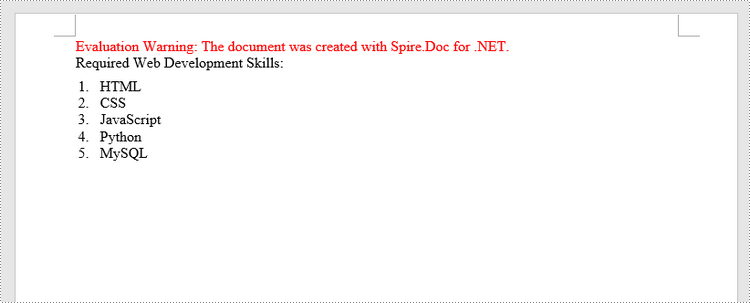
Insert a Numbered List in Word in C#, VB.NET
Spire.Doc for .NET offers the ListStyle class that you can use to create a numbered list style or a bulleted style. Then, the list style can be applied to a paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method. The steps to create a numbered list are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type through ListLevel.PatternType property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateOrderedList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a numbered list style
ListStyle listStyle = new ListStyle(document, ListType.Numbered);
listStyle.Name = "numberedList";
listStyle.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.DecimalEnclosedParen;
listStyle.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
document.ListStyles.Add(listStyle);
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Required Web Development Skills:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("HTML");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another four paragraphs and apply the numbered list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("CSS");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("JavaScript");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Python");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("MySQL");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("NumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
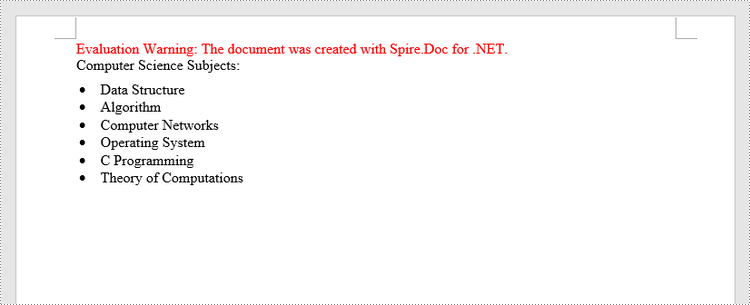
Insert a Bulleted List in Word in C#, VB.NET
The process of creating a bulleted list is similar to that of creating a numbered list. The difference is that when creating a list style, you must specify the list type as Bulleted and set a bullet symbol for it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Bulleted.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the bullet symbol through ListLevel.BulletCharacter property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateUnorderedList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a bulleted list style
ListStyle listStyle = new ListStyle(document, ListType.Bulleted);
listStyle.Name = "bulletedList";
listStyle.Levels[0].BulletCharacter = "\x00B7";
listStyle.Levels[0].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol";
listStyle.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
document.ListStyles.Add(listStyle);
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Science Subjects:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the bulleted list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Data Structure");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another five paragraphs and apply the bulleted list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Algorithm");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Networks");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Operating System");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("C Programming");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Theory of Computations");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("BulletedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
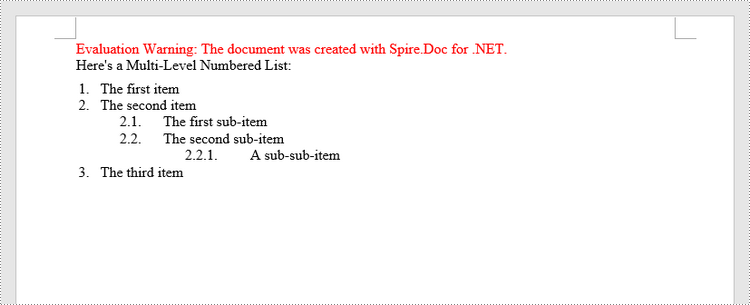
Insert a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in C#, VB.NET
A multi-level list consists of at least two different levels. Each level of a nested list is represented by the ListStyle.Levels[index] property, through which you can set the numbering type and prefix for a certain level. The following are the steps to create a multi-level numbered list in Word.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type and prefix.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateMultiLevelList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a numbered list style, specifying number prefix and pattern type of each level
ListStyle listStyle = new ListStyle(document, ListType.Numbered);
listStyle.Name = "levelstyle";
listStyle.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
listStyle.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
listStyle.Levels[1].NumberPrefix = "\x0000.";
listStyle.Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
listStyle.Levels[2].NumberPrefix = "\x0000.\x0001.";
listStyle.Levels[2].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
document.ListStyles.Add(listStyle);
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Numbered List:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another five paragraphs and apply the numbered list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ContinueListNumbering();
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("A sub-sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The third item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("MultilevelNumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
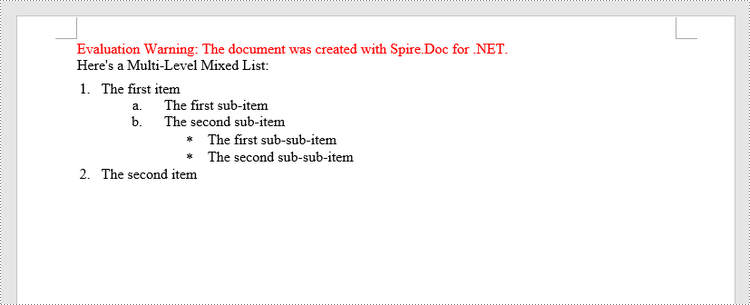
Insert a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in C#, VB.NET
In some cases, you may want to mix number and symbol bullet points in a multi-level list. To create a mixed-type list, you just need to create a numbered list style and a bulleted list style and apply them to different paragraphs. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a numbered list style and a bulleted list style.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply different list style to different paragraphs using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateMultilevelMixedList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a numbered list style
ListStyle numberedListStyle = new ListStyle(document, ListType.Numbered);
numberedListStyle.Name = "numberedStyle";
numberedListStyle.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
numberedListStyle.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
numberedListStyle.Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.LowLetter;
document.ListStyles.Add(numberedListStyle);
//Create a bulleted list style
ListStyle bulletedListStyle = new ListStyle(document, ListType.Bulleted);
bulletedListStyle.Name = "bulltedStyle";
bulletedListStyle.Levels[2].BulletCharacter = "\x002A";
bulletedListStyle.Levels[2].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol";
document.ListStyles.Add(bulletedListStyle);
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Mixed List:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another five paragraphs and apply different list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1;
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulltedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulltedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("MultilevelMixedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Get the differences by comparing two Word documents in C#/VB.NET
We have introduced how to compare two Word documents in C# and VB.NET. From Spire.Doc V8.12.14, it supports to get the differences between two Word documents in a structure list. This article will show you how to use Spire.Doc to get the differences by comparing two Word documents.
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using Spire.Doc.Formatting.Revisions;
using System;
namespace GetWordDifferences
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Load the first Word document
Document doc1 = new Document();
doc1.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx");
//Load the second Word document
Document doc2 = new Document();
doc2.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx");
//Compare the two Word documents
doc1.Compare(doc2, "Author");
foreach (Section sec in doc1.Sections)
{
foreach (DocumentObject docItem in sec.Body.ChildObjects)
{
if (docItem is Paragraph)
{
Paragraph para = docItem as Paragraph;
if (para.IsInsertRevision)
{
EditRevision insRevison = para.InsertRevision;
EditRevisionType insType = insRevison.Type;
string insAuthor = insRevison.Author;
DateTime insDateTime = insRevison.DateTime;
}
else if (para.IsDeleteRevision)
{
EditRevision delRevison = para.DeleteRevision;
EditRevisionType delType = delRevison.Type;
string delAuthor = delRevison.Author;
DateTime delDateTime = delRevison.DateTime;
}
foreach (ParagraphBase paraItem in para.ChildObjects)
{
if (paraItem.IsInsertRevision)
{
EditRevision insRevison = paraItem.InsertRevision;
EditRevisionType insType = insRevison.Type;
string insAuthor = insRevison.Author;
DateTime insDateTime = insRevison.DateTime;
}
else if (paraItem.IsDeleteRevision)
{
EditRevision delRevison = paraItem.DeleteRevision;
EditRevisionType delType = delRevison.Type;
string delAuthor = delRevison.Author;
DateTime delDateTime = delRevison.DateTime;
}
}
}
}
}
//Get the difference about revisions
DifferRevisions differRevisions = new DifferRevisions(doc1);
var insetRevisionsList = differRevisions.InsertRevisions;
var deletRevisionsList = differRevisions.DeleteRevisions;
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports Spire.Doc.Fields
Imports Spire.Doc.Formatting.Revisions
Imports System
Namespace GetWordDifferences
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Load the first Word document
Dim doc1 As Document = New Document
doc1.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
'Load the second Word document
Dim doc2 As Document = New Document
doc2.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx")
'Compare the two Word documents
doc1.Compare(doc2, "Author")
For Each sec As Section In doc1.Sections
For Each docItem As DocumentObject In sec.Body.ChildObjects
If (TypeOf docItem Is Paragraph) Then
Dim para As Paragraph = CType(docItem,Paragraph)
If para.IsInsertRevision Then
Dim insRevison As EditRevision = para.InsertRevision
Dim insType As EditRevisionType = insRevison.Type
Dim insAuthor As String = insRevison.Author
Dim insDateTime As DateTime = insRevison.DateTime
ElseIf para.IsDeleteRevision Then
Dim delRevison As EditRevision = para.DeleteRevision
Dim delType As EditRevisionType = delRevison.Type
Dim delAuthor As String = delRevison.Author
Dim delDateTime As DateTime = delRevison.DateTime
End If
For Each paraItem As ParagraphBase In para.ChildObjects
If paraItem.IsInsertRevision Then
Dim insRevison As EditRevision = paraItem.InsertRevision
Dim insType As EditRevisionType = insRevison.Type
Dim insAuthor As String = insRevison.Author
Dim insDateTime As DateTime = insRevison.DateTime
ElseIf paraItem.IsDeleteRevision Then
Dim delRevison As EditRevision = paraItem.DeleteRevision
Dim delType As EditRevisionType = delRevison.Type
Dim delAuthor As String = delRevison.Author
Dim delDateTime As DateTime = delRevison.DateTime
End If
Next
End If
Next
Next
'Get the difference about revisions
Dim differRevisions As DifferRevisions = New DifferRevisions(doc1)
Dim insetRevisionsList = differRevisions.InsertRevisions
Dim deletRevisionsList = differRevisions.DeleteRevisions
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
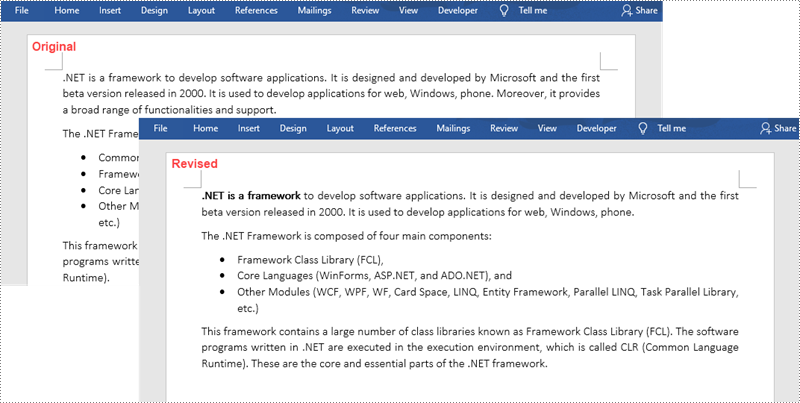
C#/VB.NET: Compare Two Word Documents
It is not uncommon at work that we may receive two versions of a Word document and face the need to find the differences between them. Document comparison is particularly important and popular in the fields of laws, regulations and education. In this article, you will learn how to compare two Word documents in C# and VB.NET by using Spire.Doc for .NET.
- Compare Two Documents and Save Result in a Third Word Document
- Compare Two Documents and Return Insertions and Deletions in Lists
Below is a screenshot of the two Word documents that’ll be compared.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
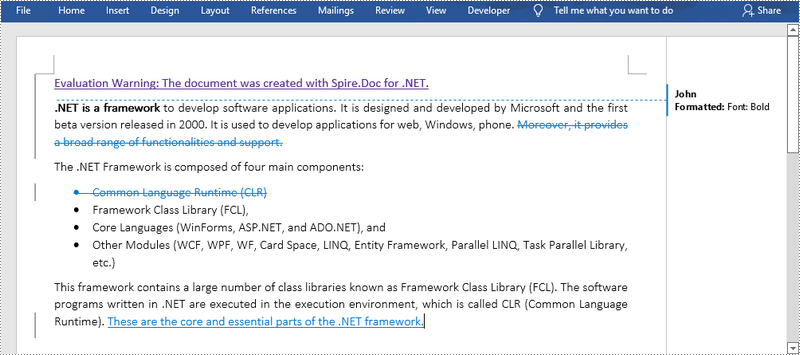
Compare Two Documents and Save Result in a Third Word Document
Saving the comparison result in a separate Word document allows us to see all the changes made to the original document, including insertions, deletions as well as modifications on formatting. The following are the steps to compare two documents and save the result in a third Word document using Spire.Doc for .NET.
- Load two Word documents separately while initialing the Document objects.
- Compare these two documents using Document.Compare() method.
- Save the result in a third Word document using ;Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
namespace CompareDocuments
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Load one Word document
Document doc1 = new Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\original.docx");
//Load the other Word document
Document doc2 = new Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\revised.docx");
//Compare two documents
doc1.Compare(doc2, "John");
//Save the differences in a third document
doc1.SaveToFile("Differences.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
doc1.Dispose();
}
}
}
Compare Two Documents and Return Insertions and Deletions in Lists
Developers may only want to obtain the insertions and deletions instead of the whole differences. The following are the steps to get insertions and deletions in two separate lists.
- Load two Word documents separately while initialing the Document objects.
- Compare two documents using Document.Compare() method.
- Get the revisions using the constructor function of the DifferRevisions ;class.
- Get a list of insertions through DifferRevisions.InsertRevisions property.
- Get a list of deletions through DifferRevisions.DeleteRevisions property.
- Loop through the elements in the two lists to get the specific insertion and deletion.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System;
namespace GetDifferencesInList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Load one Word document
Document doc1 = new Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\original.docx");
//Load the other Word document
Document doc2 = new Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\revised.docx");
//Compare the two Word documents
doc1.Compare(doc2, "Author");
//Get the revisions
DifferRevisions differRevisions = new DifferRevisions(doc1);
//Return the insertion revisions in a list
var insetRevisionsList = differRevisions.InsertRevisions;
//Return the deletion revisions in a list
var deletRevisionsList = differRevisions.DeleteRevisions;
//Create two int variables
int m = 0;
int n = 0;
//Loop through the insertion revision list
for (int i = 0; i < insetRevisionsList.Count; i++)
{
if (insetRevisionsList[i] is TextRange)
{
m += 1;
//Get the specific revision and get its content
TextRange textRange = insetRevisionsList[i] as TextRange;
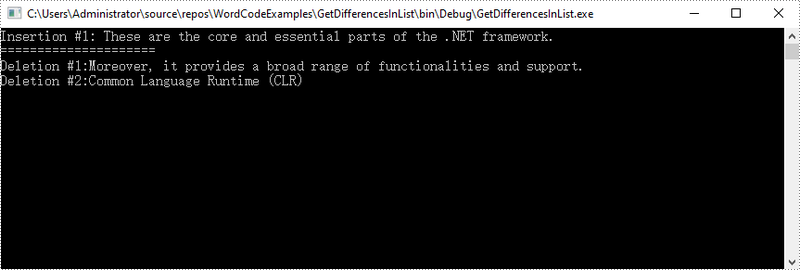
Console.WriteLine("Insertion #" + m + ":" + textRange.Text);
}
}
Console.WriteLine("=====================");
//Loop through the deletion revision list
for (int i = 0; i < deletRevisionsList.Count; i++)
{
if (deletRevisionsList[i] is TextRange)
{
n += 1;
//Get the specific revision and get its content
TextRange textRange = deletRevisionsList[i] as TextRange;
Console.WriteLine("Deletion #" + n + ":" + textRange.Text);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Insert Math Equations into Word Documents
Math equations in Word documents are essential tools for expressing mathematical concepts and relationships. Whether you are writing an academic paper, a scientific report, or any other document involving mathematical content, incorporating math equations can greatly enhance your ability to convey complex mathematical concepts and improve the visual appeal and professionalism of your document. In this article, we will explain how to insert math equations into Word documents in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Doc for .NET.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Insert Math Equations into a Word Document in C# and VB.NET
Spire.Doc for .NET allows generating math equations from LaTeX code and MathML code using OfficeMath.FromLatexMathCode(string latexMathCode) and OfficeMath.FromMathMLCode(string mathMLCode) methods. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create two string arrays from LaTeX code and MathML code.
- Create a Document instance and add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Iterate through each LaTeX code in the string array.
- Create a math equation from the LaTeX code using OfficeMath.FromLatexMathCode(string latexMathCode) method.
- Add a paragraph to the section, then add the math equation to the paragraph using Paragraph.Items.Add() method.
- Iterate through each MathML code in the string array.
- Create a math equation from the MathML code using OfficeMath.FromMathMLCode(string mathMLCode) method.
- Add a paragraph to the section, then add the math equation to the paragraph using Paragraph.Items.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields.OMath;
namespace AddMathEquations
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a string array from LaTeX code
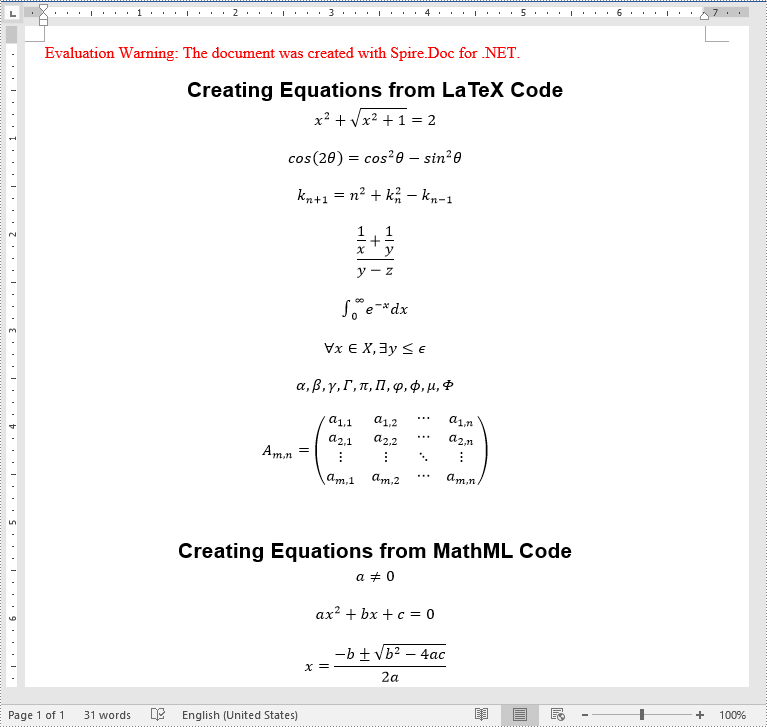
string[] latexMathCode = {
"x^{2}+\\sqrt{x^{2}+1}=2",
"\\cos (2\\theta) = \\cos^2 \\theta - \\sin^2 \\theta",
"k_{n+1} = n^2 + k_n^2 - k_{n-1}",
"\\frac {\\frac {1}{x}+ \\frac {1}{y}}{y-z}",
"\\int_0^ \\infty \\mathrm {e}^{-x} \\, \\mathrm {d}x",
"\\forall x \\in X, \\quad \\exists y \\leq \\epsilon",
"\\alpha, \\beta, \\gamma, \\Gamma, \\pi, \\Pi, \\phi, \\varphi, \\mu, \\Phi",
"A_{m,n} = \\begin{pmatrix} a_{1,1} & a_{1,2} & \\cdots & a_{1,n} \\\\ a_{2,1} & a_{2,2} & \\cdots & a_{2,n} \\\\ \\vdots & \\vdots & \\ddots & \\vdots \\\\ a_{m,1} & a_{m,2} & \\cdots & a_{m,n} \\end{pmatrix}",
};
//Create a string array from MathML code
string[] mathMLCode = {
"<math xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML\"><mi>a</mi><mo>≠</mo><mn>0</mn></math>",
"<math xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML\"><mi>a</mi><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>+</mo><mi>b</mi><mi>x</mi><mo>+</mo><mi>c</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>0</mn></math>",
"<math xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML\"><mi>x</mi><mo>=</mo><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mo>−</mo><mi>b</mi><mo>±</mo><msqrt><msup><mi>b</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>−</mo><mn>4</mn><mi>a</mi><mi>c</mi></msqrt></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn><mi>a</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>",
};
//Create a Document instance
Document doc = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = doc.AddSection();
//Add a paragraph to the section
Paragraph textPara = section.AddParagraph();
textPara.AppendText("Creating Equations from LaTeX Code");
textPara.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading1);
textPara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
//Iterate through each LaTeX code in the string array
for (int i = 0; i < latexMathCode.Length; i++)
{
//Create a math equation from the LaTeX code
OfficeMath officeMath = new OfficeMath(doc);
officeMath.FromLatexMathCode(latexMathCode[i]);
//Add the math equation to the section
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.Items.Add(officeMath);
section.AddParagraph();
}
section.AddParagraph();
//Add a paragraph to the section
textPara = section.AddParagraph();
textPara.AppendText("Creating Equations from MathML Code");
textPara.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading1);
textPara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
//Iterate through each MathML code in the string array
for (int j = 0; j < mathMLCode.Length; j++)
{
//Create a math equation from the MathML code
OfficeMath officeMath = new OfficeMath(doc);
officeMath.FromMathMLCode(mathMLCode[j]);
//Add the math equation to the section
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.Items.Add(officeMath);
section.AddParagraph();
}
//Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("AddMathEquations.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Add checkbox and picture content control to word document in C#
Besides the Combo Box, Text, Date Picker and Drop-Down List content controls, Checkbox and picture content control also are the mostly used content control in word document. Spire.Doc supports to add many kinds of content controls to the word document. This article will show you how to add checkbox and picture content control to word document by Spire.Doc for .NET.
Code snippets of how to add checkbox and picture content control:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
namespace AddCheckbox
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a new word document
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section to the document
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Add a document to the section
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
//Add checkbox content control
StructureDocumentTagInline sdt = new StructureDocumentTagInline(document);
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
sdt = new StructureDocumentTagInline(document);
sdt.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt);
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.CheckBox;
SdtCheckBox scb = new SdtCheckBox();
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = scb;
TextRange tr = new TextRange(document);
tr.CharacterFormat.FontName = "MS Gothic";
tr.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
sdt.ChildObjects.Add(tr);
scb.Checked = true;
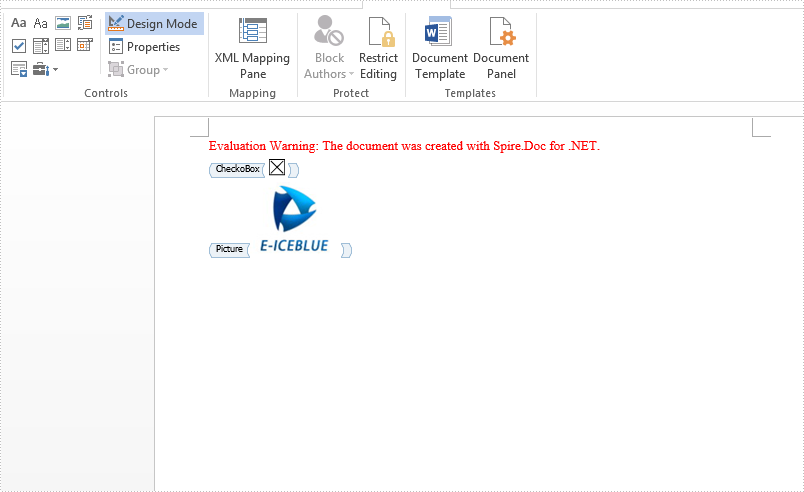
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "CheckoBox";
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Checkbox";
//Add picture content control
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
sdt = new StructureDocumentTagInline(document);
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt);
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = new SdtPicture();
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Picture";
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Picture";
DocPicture pic = new DocPicture(document) { Width = 10, Height = 10 };
pic.LoadImage(Image.FromFile("Logo.jpg"));
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(pic);
document.SaveToFile("Sample.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
}
}
}
Effective screenshot after adding checkbox and picture content control to word document:
C#/VB.NET: Detect and Remove VBA Macros from Word Documents
VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) macros are small programs that can be embedded within Microsoft Word documents to automate repetitive tasks, add interactivity to documents, and perform other useful functions. While macros can be beneficial in many situations, they can also pose a security risk if the code is malicious or contains malware. By removing VBA macros from Word documents, you can reduce the risk of security breaches and malware infections. In this article, you will learn how to detect and remove VBA macros from Word documents in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Doc for .NET library.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Detect and Remove VBA Macros from Word Documents in C# and VB.NET
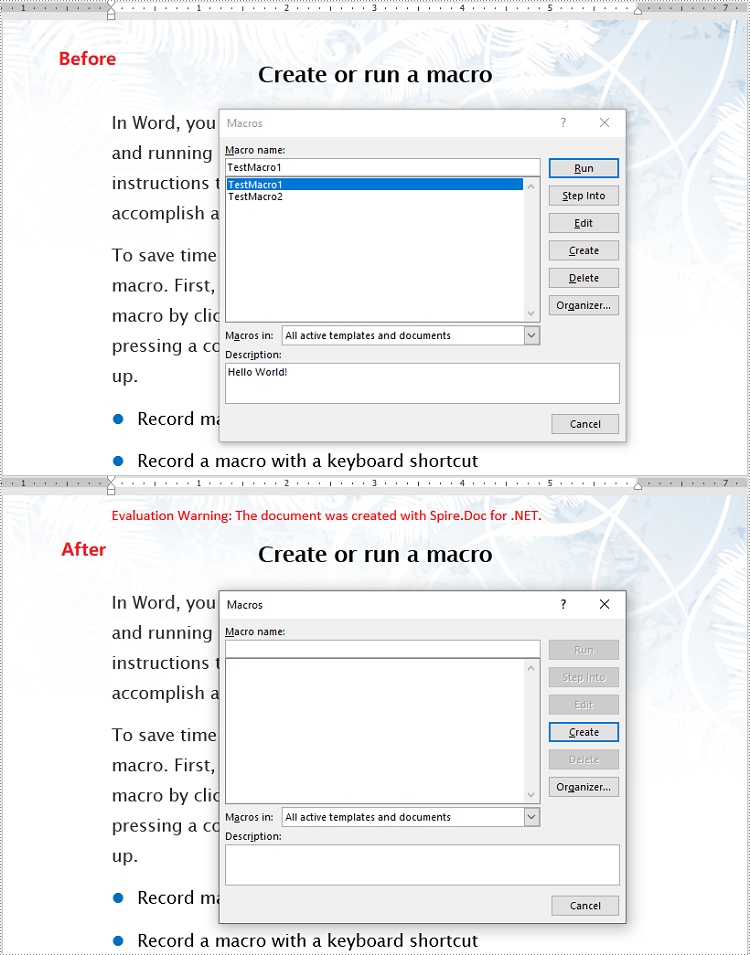
You can use the Document.IsContainMacro property to detect whether a Word document contains VBA macros. If any macros are detected, you can use the Document.ClearMacros() method to easily remove them from the document.
The following steps show how to detect and remove VBA macros from a Word document using Spire.Doc for .NET:
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile(string fileName) method.
- Detect if the document contains VBA macros using the Document.IsContainMacro property.
- If any macros are detected, remove them from the document using Document.ClearMacros() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile(string fileName, FileFormat fileFormat) method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
namespace RemoveVBAMacros
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Initialize an instance of the Document class
Document document = new Document();
//Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Input.docm");
//Detect if the document contains macros
if (document.IsContainMacro)
{
//Remove the macros from the document
document.ClearMacros();
}
//Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveMacros.docm", FileFormat.Docm);
document.Close();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.