Java: Copy Content from One Word Document to Another
Transferring content between Microsoft Word documents is a frequent task for many users. Whether you need to consolidate information spread across multiple files or quickly reuse existing text and other elements, the ability to effectively copy and paste between documents can save you time and effort.
In this article, you will learn how to copy content from one Word document to another using Java and Spire.Doc for Java.
- Copy Specified Paragraphs from One Word Document to Another
- Copy a Section from One Word Document to Another
- Copy the Entire Document and Append it to Another
- Create a Copy of a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Copy Specified Paragraphs from One Word Document to Another in Java
Spire.Doc for Java provides a flexible way to copy content between Microsoft Word documents. This is achieved by cloning individual paragraphs and then adding those cloned paragraphs to a different document.
To copy specific paragraphs from one Word document to another, you can follow these steps:
- Load the source document into a Document object.
- Load the target document into a separate Document object.
- Identify the paragraphs you want to copy from the source document.
- Create copies of those selected paragraphs using Paragraph.deepClone() method
- Add the cloned paragraphs to the target document using ParagraphCollection.add() method.
- Save the updated target document to a new Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
public class CopyParagraphs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document sourceDoc = new Document();
// Load the source file
sourceDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\source.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = sourceDoc.getSections().get(0);
// Get the specified paragraphs from the source file
Paragraph p1 = section.getParagraphs().get(2);
Paragraph p2 = section.getParagraphs().get(3);
// Create another Document object
Document targetDoc = new Document();
// Load the target file
targetDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Get the last section
Section lastSection = targetDoc.getLastSection();
// Add the paragraphs from the source file to the target file
lastSection.getParagraphs().add((Paragraph)p1.deepClone());
lastSection.getParagraphs().add((Paragraph)p2.deepClone());
// Save the target file to a different Word file
targetDoc.saveToFile("CopyParagraphs.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
sourceDoc.dispose();
targetDoc.dispose();
}
}
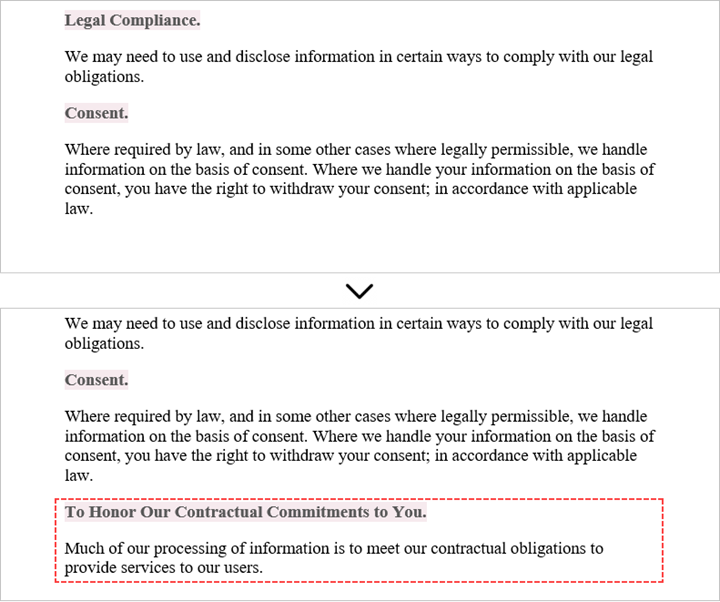
Copy a Section from One Word Document to Another in Java
When copying content between Microsoft Word documents, it's important to consider that a section can contain not only paragraphs, but also other elements like tables. To successfully transfer an entire section from one document to another, you need to iterate through all the child objects within the section and add them individually to a specific section in the target document.
The steps to copy a section between different Word documents are as follows:
- Create Document objects to load the source file and the target file, respectively.
- Get the specified section from the source document.
- Iterate through the child objects within the section.
- Clone a specific child object using DocumentObject.deepClone() method.
- Add the cloned child objects to a designated section in the target document using DocumentObjectCollection.add() method.
- Save the updated target document to a new file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.DocumentObject;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
public class CopySection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document sourceDoc = new Document();
// Load the source file
sourceDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\source.docx");
// Get the specified section from the source file
Section section = sourceDoc.getSections().get(0);
// Create another Document object
Document targetDoc = new Document();
// Load the target file
targetDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Get the last section of the target file
Section lastSection = targetDoc.getLastSection();
// Iterate through the child objects in the selected section
for (int i = 0; i < section.getBody().getChildObjects().getCount(); i++) {
// Get a specific child object
DocumentObject childObject = section.getBody().getChildObjects().get(i);
// Add the child object to the last section of the target file
lastSection.getBody().getChildObjects().add(childObject.deepClone());
}
// Save the target file to a different Word file
targetDoc.saveToFile("CopySection.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
sourceDoc.dispose();
targetDoc.dispose();
}
}

Copy the Entire Document and Append it to Another in Java
Copying the full contents from one Microsoft Word document into another can be achieved using the Document.insertTextFromFile() method. This method enables you to seamlessly append the contents of a source document to a target document.
The steps to copy an entire document and append it to another are as follows:
- Create a Document object to represent the target file.
- Load the target file from the given file path.
- Insert the content of a different Word document into the target file using Document.insertTextFromFile() method.
- Save the updated target file to a new Word document.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
public class CopyEntireDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Specify the path of the source document
String sourceFile = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\source.docx";
// Create a Document object
Document targetDoc = new Document();
// Load the target file
targetDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Insert content of the source file to the target file
targetDoc.insertTextFromFile(sourceFile, FileFormat.Docx);
// Save the target file to a different Word file
targetDoc.saveToFile("CopyEntireDocument.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
targetDoc.dispose();
}
}
Create a Copy of a Word Document in Java
Spire.Doc for Java provides a straightforward way to create a duplicate of a Microsoft Word document by using the Document.deepClone() method.
To make a copy of a Word document, follow these steps:
- Create a Document object to relisent the source document.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Create a copy of the document using Document.deepClone() method.
- Save the cloned document to a new Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
public class DuplicateDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document sourceDoc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
sourceDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Clone the document
Document newDoc = sourceDoc.deepClone();
// Save the cloned document as a docx file
newDoc.saveToFile("Copy.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
sourceDoc.dispose();
newDoc.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Create Column Charts in Word Documents
Column charts, also known as bar charts, provide a visual comparison of data points across different categories. Whether you're summarizing sales figures, tracking project milestones, or visualizing survey results, column charts in Word provide a powerful way to translate complex data into an accessible, engaging format within your written materials.
In this article, you will learn how to create a clustered column chart and a stacked column chart in a Word document using Spire.Doc for Java.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Create a Clustered Column Chart in Word in Java
To insert a chart into a Microsoft Word document, you can use the Paragraph.appendChart(ChartType chartType, float width, float height) method. The ChartType enumeration provides various pre-defined chart types available in MS Word. To create a clustered column chart, you would specify the chart type as Column.
The steps to add a clustered column chart to a Word document using Java are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section and a paragraph to the document.
- Add a clustered column chart to the paragraph using Paragraph.appendChart() method.
- Add series to the chart using Chart.getSeries().add() method.
- Set the chart title using Chart.getTilte().setText() method.
- Set other attributes of the chart using the methods available in the Chart object.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.fields.ShapeObject;
import com.spire.doc.fields.shapes.charts.*;
public class CreateClusteredColumnChart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Add a section
Section section = document.addSection();
// Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.addParagraph();
// Add a column chart
ShapeObject shape = paragraph.appendChart(ChartType.Column, 490, 250);
// Get the chart
Chart chart = shape.getChart();
// Clear the default data
chart.getSeries().clear();
// Add a series including series name, category names, and series values to chart
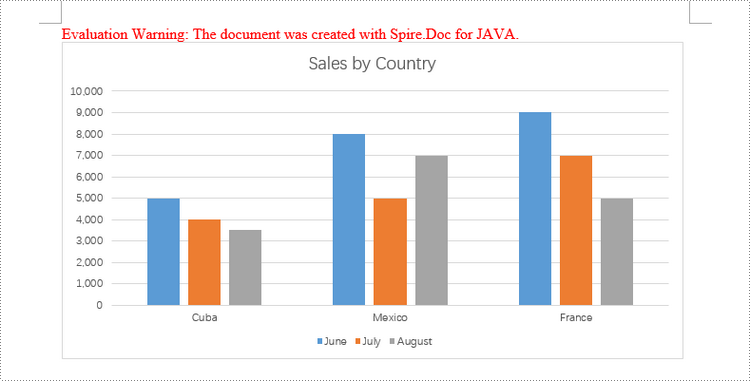
chart.getSeries().add("June",
new String[] { "Cuba", "Mexico", "France"},
new double[] { 5000, 8000, 9000 });
// Add two more series
chart.getSeries().add("July",
new String[] { "Cuba", "Mexico", "France"},
new double[] { 4000, 5000, 7000 });
chart.getSeries().add("August",
new String[] { "Cuba", "Mexico", "France"},
new double[] { 3500, 7000, 5000 });
// Set the chart title
chart.getTitle().setText("Sales by Country");
// Set the number format of the Y-axis
chart.getAxisY().getNumberFormat().setFormatCode("#,##0");
// Set the legend position
chart.getLegend().setPosition(LegendPosition.Bottom);
// Save to file
document.saveToFile("ClusteredColumnChart.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
document.dispose();
}
}
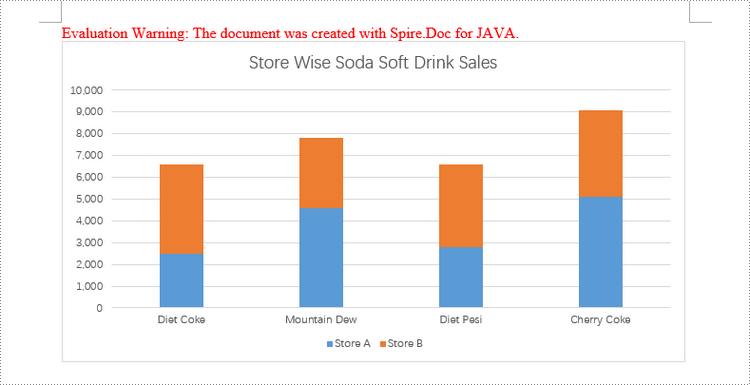
Create a Stacked Column Chart in Word in Java
Creating a stacked column chart in a Word document follows a similar process to the clustered column chart. The only difference is specifying the chart type as Column_Stacked instead of Column.
The detailed steps to add a stacked column chart are:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section and a paragraph to the document.
- Add a stacked column chart to the paragraph using Paragraph.appendChart() method.
- Add series to the chart using Chart.getSeries().add() method.
- Set the chart title using Chart.getTilte().setText() method.
- Set other attributes of the chart using the methods available in the Chart object.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.fields.ShapeObject;
import com.spire.doc.fields.shapes.charts.Chart;
import com.spire.doc.fields.shapes.charts.ChartType;
import com.spire.doc.fields.shapes.charts.LegendPosition;
public class CreateStackedColumnChart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.addSection();
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.addParagraph();
//Add a stacked column chart
ShapeObject shape = paragraph.appendChart(ChartType.Column_Stacked, 490, 250);
//Get the chart
Chart chart = shape.getChart();
//Clear the default data
chart.getSeries().clear();
//Add a series including series name, category names, and series values to chart
chart.getSeries().add("Store A",
new String[] { "Diet Coke", "Mountain Dew", "Diet Pesi", "Cherry Coke" },
new double[] { 2500, 4600, 2800, 5100 });
//Add another series
chart.getSeries().add("Store B",
new String[] { "Diet Coke", "Mountain Dew", "Diet Pesi", "Cherry Coke" },
new double[] { 4100, 3200, 3800, 4000 });
//Set the chart title
chart.getTitle().setText("Store Wise Soda Soft Drink Sales");
//Set the number format of the Y-axis
chart.getAxisY().getNumberFormat().setFormatCode("#,##0");
//Set the legend position
chart.getLegend().setPosition(LegendPosition.Bottom);
//Save to file
document.saveToFile("StackedColumnChart.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
document.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Edit a Word Document
Editing a Word document is a common task that many people encounter in their daily lives, whether it's for work, school, or personal projects. From correcting spelling and grammar errors to rearranging content and formatting the document, the ability to edit a Word document efficiently is a valuable skill.
In this article, you will learn how to programmatically edit or modify a Word document using Spire.Doc for Java.
- Modify Text in a Word Document
- Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document
- Add New Elements to a Word Document
- Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
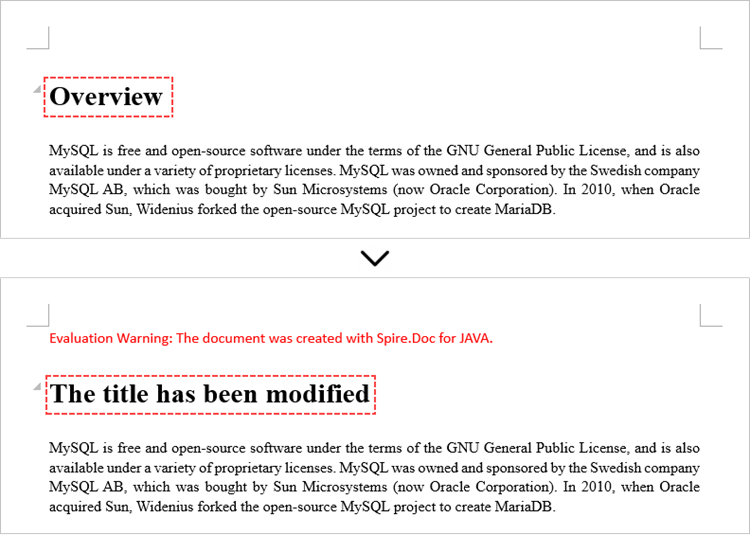
Modify Text in a Word Document in Java
To retrieve the paragraph from a particular section, you can use the Section.getParagraphs().get() method. Once you have the target paragraph, you can then update its text content by calling the Paragraph.setText() method and passing in the new text you want to assign.
The following are the steps modify text in a Word document using Java:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.getSections().get() method.
- Get a specific paragraph using Section.getParagraphs().get() method.
- Reset the text of the paragraph using Paragraph.setText() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
public class ModifyText {
https://ok.166.net/reunionpub/2023-06-06/ntesgod_cms/1686032662375_vfdeuv.png
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = document.getSections().get(0);
// Get a specific paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.getParagraphs().get(0);
// Modify the text of the paragraph
paragraph.setText("The title has been modified");
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.saveToFile("ModifyText.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.dispose();
}
}
Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document in Java
To modify the formatting of specific text within a paragraph, you first need to access the target paragraph object. Once you have the paragraph, you can then iterate through its child elements to locate the individual text ranges.
For each text range found, you can update the formatting by using the methods under the CharacterFormat object. This allows you to set properties like font name, size, color, and other text-level formatting options for the selected text.
The steps to change text formatting in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.getSections().get() method.
- Get a specific paragraph using Section.getParagraphs().get() method.
- Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph.
- Determine if a child object is a text range.
- Get a specific text range.
- Reset the text formatting using the methods under the CharacterFormat object.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.fields.TextRange;
import java.awt.*;
public class ChangeTextFormatting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = document.getSections().get(0);
// Get a specific paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.getParagraphs().get(1);
// Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.getChildObjects().getCount(); i++)
{
// Determine if a child object is text range
if (paragraph.getChildObjects().get(i) instanceof TextRange)
{
// Get a specific text range
TextRange textRange = (TextRange)paragraph.getChildObjects().get(i);
// Reset font name for it
textRange.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Corbel Light");
// Reset font size for it
textRange.getCharacterFormat().setFontSize(11);
// Reset text color for it
textRange.getCharacterFormat().setTextColor(Color.blue);
// Apply italic to the text range
textRange.getCharacterFormat().setItalic(true);
}
}
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.saveToFile("ChangeFont.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.dispose();
}
}
Add New Elements to a Word Document in Java
When working with Word documents, the paragraph serves as the foundational unit for incorporating diverse elements like text, images, lists, and charts. To introduce a new paragraph within a specific section, you can leverage the Section.addParagraph() method.
Once the paragraph has been added, you can then proceed to add various other elements to it by utilizing the methods available within the Paragraph object.
The following are the steps to add new elements (text and images) to a Word document using Java:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.getSections() method.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.addParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph using Paragraph.appendText() method.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.appendPicture() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.documents.ParagraphStyle;
public class AddNewElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get the last section
Section lastSection = document.getLastSection();
// Add a paragraph to the section
Paragraph paragraph = lastSection.addParagraph();
// Add text to the paragraph
paragraph.appendText("This text and the image shown below are added programmatically using Spire.Doc for Java.");
// Add an image to the paragraph
paragraph.appendPicture("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png");
// Create a paragraph style
ParagraphStyle style = new ParagraphStyle(document);
style.setName("FontStyle");
style.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Times New Roman");
style.getCharacterFormat().setFontSize(12);
document.getStyles().add(style);
// Apply the style to the paragraph
paragraph.applyStyle(style.getName());
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.saveToFile("AddNewElements.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.dispose();
}
}

Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document in Java
To remove a specific paragraph from the collection of paragraphs within a document, you can call the ParagraphCollection.removeAt() method. This method takes the index of the paragraph you wish to remove as an argument, allowing you to selectively delete the desired paragraph from the document.
The steps to remove paragraphs from a Word document using Java are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.getSections().get() method.
- Remove a specific paragraph from the section using ParagraphCollection.removeAt() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
public class RemoveParagraph {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = document.getSections().get(0);
// Remove a specific paragraph
section.getParagraphs().removeAt(0);
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.saveToFile("RemoveParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Modify Content Controls in Word documents
In a Word document, content controls are special elements that can be used to add interactivity and dynamic content, making the document more interactive and functional. Through content controls, users can easily insert, delete, or modify content in specific sections without altering the overall structure of the document, making it easier to create various types of documents and improve efficiency. This article will introduce how to use Spire.Doc for Java to modify content controls in Word documents within a Java project.
- Modify Content Controls in the Body using Java
- Modify Content Controls within Paragraphs using Java
- Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Rows using Java
- Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Cells using Java
- Modify Content Controls within Table Cells using Java
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Modify Content Controls in the Body using Java
In Spire.Doc, to modify content controls in the body, you need to work with objects of the StructureDocumentTag type. By iterating through the collection of child objects in Section.getBody(), you can find objects of type StructureDocumentTag and make the necessary changes. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section in the document using Section.getBody().
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the body using Body.getChildObjects() to find objects of type StructureDocumentTag.
- Access the collection of child objects in StructureDocumentTag.getChildObjects() and perform the required modifications based on the type of the child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import java.util.*;
public class ModifyContentControlInBody {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from file
doc.loadFromFile("Sample1.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.getSections().get(0).getBody();
// Create lists for paragraphs and tables
List<Paragraph> paragraphs = new ArrayList<>();
List<Table> tables = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < body.getChildObjects().getCount(); i++) {
// Get the document object
DocumentObject documentObject = body.getChildObjects().get(i);
// If it is a StructureDocumentTag object
if (documentObject instanceof StructureDocumentTag) {
StructureDocumentTag structureDocumentTag = (StructureDocumentTag) documentObject;
// If the tag is "c1" or the alias is "c1"
if (structureDocumentTag.getSDTProperties().getTag().equals("c1") || structureDocumentTag.getSDTProperties().getAlias().equals("c1")) {
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTag.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++) {
// If it is a paragraph object
if (structureDocumentTag.getChildObjects().get(j) instanceof Paragraph) {
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph) structureDocumentTag.getChildObjects().get(j);
paragraphs.add(paragraph);
}
// If it is a table object
if (structureDocumentTag.getChildObjects().get(j) instanceof Table) {
Table table = (Table) structureDocumentTag.getChildObjects().get(j);
tables.add(table);
}
}
}
}
}
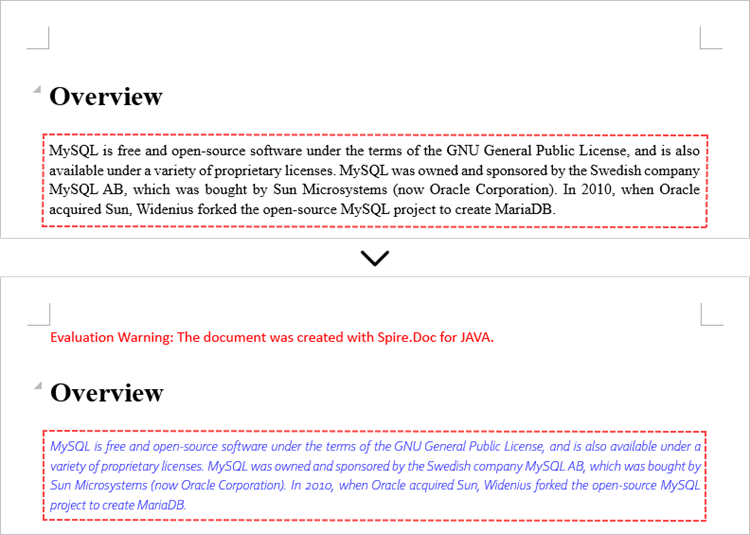
// Modify the text content of the first paragraph
paragraphs.get(0).setText("Chengdu E-iceblue Co., Ltd. is committed to providing JAVA component development products for developers.");
// Reset the cells of the first table to 5 rows and 4 columns
tables.get(0).resetCells(5, 4);
// Save the modified document to a file
doc.saveToFile("Modify Content Controls in Word Document Body.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Close the document and release document resources
doc.close();
doc.dispose();
}
}
Modify Content Controls within Paragraphs using Java
In Spire.Doc, to modify content controls within a paragraph, you need to use objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline. The specific steps involve iterating through the collection of child objects in a paragraph, finding objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline, and then making the necessary modifications. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section using Section.getBody().
- Retrieve the first paragraph of the body using Body.getParagraphs().get(0).
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the paragraph using Paragraph.getChildObjects() to find objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline.
- Access the collection of child objects in StructureDocumentTagInline using StructureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects() and perform the necessary modifications based on the type of child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
public class ModifyContentControlInParagraph {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from a file
doc.loadFromFile("Sample2.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.getSections().get(0).getBody();
// Get the first paragraph of the body
Paragraph paragraph = body.getParagraphs().get(0);
// Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.getChildObjects().getCount(); i++) {
// Check if the child object is of type StructureDocumentTagInline
if (paragraph.getChildObjects().get(i) instanceof StructureDocumentTagInline) {
// Convert the child object to StructureDocumentTagInline type
StructureDocumentTagInline structureDocumentTagInline = (StructureDocumentTagInline) paragraph.getChildObjects().get(i);
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of the document tag is "text1"
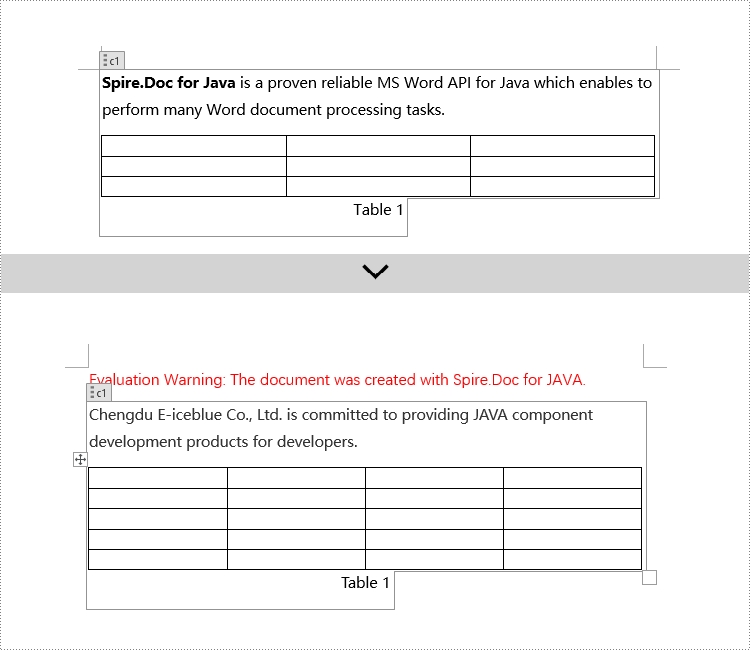
if (structureDocumentTagInline.getSDTProperties().getTag().equals("text1") || structureDocumentTagInline.getSDTProperties().getAlias().equals("text1")) {
// Iterate through the child objects in the StructureDocumentTagInline object
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++) {
// Check if the child object is a TextRange object
if (structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().get(j) instanceof TextRange) {
// Convert the child object to TextRange type
TextRange range = (TextRange) structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().get(j);
// Set the text content to the specified content
range.setText("Word97-2003, Word2007, Word2010, Word2013, Word2016, and Word2019");
}
}
}
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of the document tag is "logo1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.getSDTProperties().getTag().equals("logo1") || structureDocumentTagInline.getSDTProperties().getAlias().equals("logo1")) {
// Iterate through the child objects in the StructureDocumentTagInline object
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++) {
// Check if the child object is an image
if (structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().get(j) instanceof DocPicture) {
// Convert the child object to DocPicture type
DocPicture docPicture = (DocPicture) structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().get(j);
// Load the specified image
docPicture.loadImage("Doc-Java.png");
// Set the width and height of the image
docPicture.setWidth(100);
docPicture.setHeight(100);
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.saveToFile("Modified Content Controls in Paragraphs of a Word Document.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Close the document and release document resources
doc.close();
doc.dispose();
}
}

Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Rows using Java
In Spire.Doc, to modify content controls in table rows, you need to iterate through the collection of table's child objects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagRow, and then make the necessary changes. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section in the document using Section.getBody().
- Get the first table in the body using Body.getTables().get(0).
- Iterate through the table's child objects collection using Table.getChildObjects() to find objects of type StructureDocumentTagRow.
- Access the cell collection of the table row content controls using StructureDocumentTagRow.getCells(), and then perform the required modifications on the cell contents.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ModifyTextContentControlInTableRow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a document from a file
doc.loadFromFile("Sample3.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.getSections().get(0).getBody();
// Get the first table
Table table = body.getTables().get(0);
// Iterate through the child objects in the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.getChildObjects().getCount(); i++) {
// Check if the child object is of type StructureDocumentTagRow
if (table.getChildObjects().get(i) instanceof StructureDocumentTagRow) {
// Convert the child object to a StructureDocumentTagRow object
StructureDocumentTagRow structureDocumentTagRow = (StructureDocumentTagRow) table.getChildObjects().get(i);
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of the StructureDocumentTagRow is "row1"
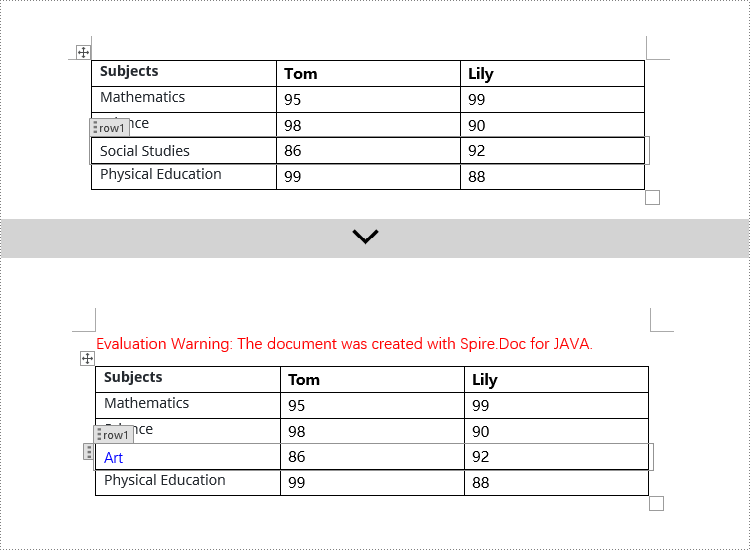
if (structureDocumentTagRow.getSDTProperties().getTag().equals("row1") || structureDocumentTagRow.getSDTProperties().getAlias().equals("row1")) {
// Clear the paragraphs in the cell
structureDocumentTagRow.getCells().get(0).getParagraphs().clear();
// Add a paragraph in the cell and set the text
TextRange textRange = structureDocumentTagRow.getCells().get(0).addParagraph().appendText("Art");
textRange.getCharacterFormat().setTextColor(Color.BLUE);
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a file
doc.saveToFile("ModifiedTableRowContentControl.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Close the document and release the document resources
doc.close();
doc.dispose();
}
}
Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Cells using Java
In Spire.Doc, to manipulate content control objects in table cells, you need to use a specific type of object called StructureDocumentTagCell. This can be done by examining the collection of child objects in TableRow.getChildObjects(), finding objects of type StructureDocumentTagCell, and then performing the necessary operations. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section in the document using Section.getBody().
- Get the first table in the body using Body.getTables().get(0).
- Iterate through the collection of table rows using Table.getRows() and access each TableRow object.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the table row using TableRow.getChildObjects() to find objects of type StructureDocumentTagCell.
- Access the collection of paragraphs in StructureDocumentTagCell.getParagraphs() for the content control in the table cell and perform the necessary modifications on the content.
- Save the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ModifyTextContentControlInTableCell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.loadFromFile("Sample4.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.getSections().get(0).getBody();
// Get the first table in the document
Table table = body.getTables().get(0);
// Iterate through the rows of the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.getRows().getCount(); i++) {
// Iterate through the child objects in each row
for (int j = 0; j < table.getRows().get(i).getChildObjects().getCount(); j++) {
// Check if the child object is a StructureDocumentTagCell
if (table.getRows().get(i).getChildObjects().get(j) instanceof StructureDocumentTagCell) {
// Convert the child object to StructureDocumentTagCell type
StructureDocumentTagCell structureDocumentTagCell = (StructureDocumentTagCell) table.getRows().get(i).getChildObjects().get(j);
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of structureDocumentTagCell is "cell1"
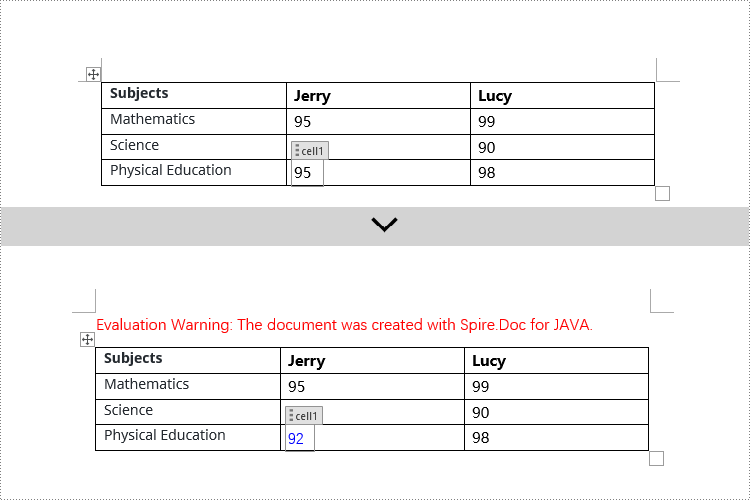
if (structureDocumentTagCell.getSDTProperties().getTag().equals("cell1") || structureDocumentTagCell.getSDTProperties().getAlias().equals("cell1")) {
// Clear the paragraphs in the cell
structureDocumentTagCell.getParagraphs().clear();
// Add a new paragraph and append text to it
TextRange textRange = structureDocumentTagCell.addParagraph().appendText("92");
textRange.getCharacterFormat().setTextColor(Color.BLUE);
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.saveToFile("ModifiedTableCellContentControl.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Close the document and release the document resources
doc.close();
doc.dispose();
}
}
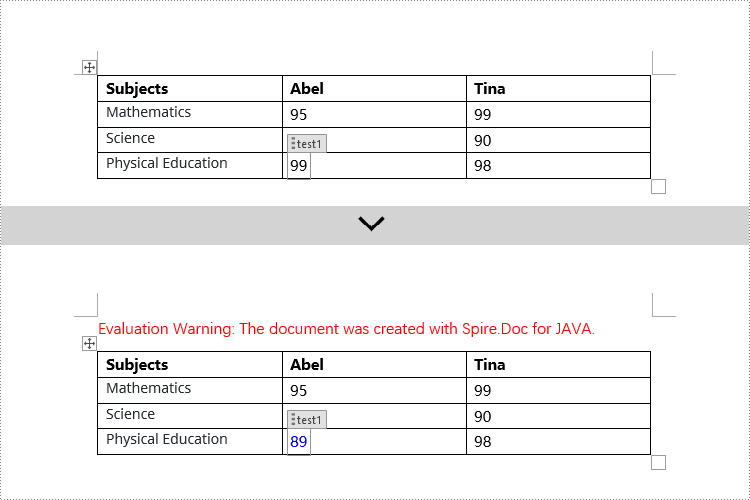
Modify Content Controls within Table Cells using Java
This example demonstrates how to modify content controls in paragraphs within table cells. Firstly, you need to access the collection of paragraphs in a cell using TableCell.getParagraphs(), then iterate through the child objects collection of each paragraph using Paragraph.getChildObjects(), and search for objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline within it for modification.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section in the document using Section.getBody().
- Get the first table in the body using Body.getTables().get(0).
- Iterate through the collection of table rows using Table.getRows(), accessing each TableRow object.
- Iterate through the collection of cells in a row using TableRow.getCells(), accessing each TableCell object.
- Iterate through the collection of paragraphs in a cell using TableCell.getParagraphs(), accessing each Paragraph object.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in a paragraph using Paragraph.getChildObjects(), looking for objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline.
- Access the collection of child objects in StructureDocumentTagInline using StructureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects(), and perform the necessary modification based on the type of child object.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ModifyTextContentControlInParagraphOfTableCell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from a file
doc.loadFromFile("Sample5.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.getSections().get(0).getBody();
// Get the first table
Table table = body.getTables().get(0);
// Iterate through the rows of the table
for (int r = 0; r < table.getRows().getCount(); r++) {
// Iterate through the cells in the table row
for (int c = 0; c < table.getRows().get(r).getCells().getCount(); c++) {
// Iterate through the paragraphs in the cell
for (int p = 0; p < table.getRows().get(r).getCells().get(c).getParagraphs().getCount(); p++) {
// Get the paragraph object
Paragraph paragraph = table.getRows().get(r).getCells().get(c).getParagraphs().get(p);
// Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.getChildObjects().getCount(); i++) {
// Check if the child object is of type StructureDocumentTagInline
if (paragraph.getChildObjects().get(i) instanceof StructureDocumentTagInline) {
// Convert it to a StructureDocumentTagInline object
StructureDocumentTagInline structureDocumentTagInline = (StructureDocumentTagInline) paragraph.getChildObjects().get(i);
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of StructureDocumentTagInline is "test1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.getSDTProperties().getTag().equals("test1") || structureDocumentTagInline.getSDTProperties().getAlias().equals("test1")) {
// Iterate through the child objects of StructureDocumentTagInline
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++) {
// Check if the child object is of type TextRange
if (structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().get(j) instanceof TextRange) {
// Convert it to a TextRange object
TextRange textRange = (TextRange) structureDocumentTagInline.getChildObjects().get(j);
// Set the text content
textRange.setText("89");
// Set the text color
textRange.getCharacterFormat().setTextColor(Color.BLUE);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.saveToFile("ModifiedContentControlInParagraphsOfTableCell.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Close the document and release document resources
doc.close();
doc.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Create a Table Of Contents for a Newly Created Word Document
Creating a table of contents in a Word document can help readers quickly understand the structure and content of the document, thereby enhancing its readability. The creation of a table of contents also aids authors in organizing the document's content, ensuring a clear structure and strong logical flow. When modifications or additional content need to be made to the document, the table of contents can help authors quickly locate the sections that require editing. This article will explain how to use Spire.Doc for Java to create a table of contents for a newly created Word document in a Java project.
- Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Heading Styles
- Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Outline Level Styles
- Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Image Captions
- Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Table Captions
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Heading Styles
In Spire.Doc, creating a table of contents using heading styles is the default method for generating a table of contents. By applying different levels of heading styles to sections and subsections in the document, the table of contents is automatically generated. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.addSection() method.
- Add a paragraph using the Section.addParagraph() method.
- Create a table of contents object using the Paragraph.appendTOC(int lowerLevel, int upperLevel) method.
- Create a CharacterFormat character format object and set the font.
- Apply a heading style to the paragraph using the Paragraph.applyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading_1) method.
- Add text content using the Paragraph.appendText() method.
- Set character formatting for the text using the TextRange.applyCharacterFormat() method.
- Update the table of contents using the Document.updateTableOfContents() method.
- Save the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import com.spire.doc.formatting.*;
public class CreateTOCByHeadingStyle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Add a section to the document
Section section = doc.addSection();
// Add a table of contents paragraph
Paragraph TOCparagraph = section.addParagraph();
TOCparagraph.appendTOC(1, 3);
// Create a character format object and set the font
CharacterFormat characterFormat1 = new CharacterFormat(doc);
characterFormat1.setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
// Create another character format object and set the font and font size
CharacterFormat characterFormat2 = new CharacterFormat(doc);
characterFormat2.setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
characterFormat2.setFontSize(12);
// Add a paragraph with Heading 1 style
Paragraph paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading_1);
// Add text and apply character format
TextRange textRange1 = paragraph.appendText("Overview");
textRange1.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat1);
// Add regular content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
TextRange textRange2 = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java is a professional Word API that empowers Java applications to create, convert, manipulate and print Word documents without dependency on Microsoft Word.");
textRange2.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat2);
// Add a paragraph with Heading 1 style
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading_1);
textRange1 = paragraph.appendText("MAIN FUNCTION");
textRange1.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat1);
// Add a paragraph with Heading 2 style
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading_2);
textRange1 = paragraph.appendText("Only Spire.Doc for Java, No Microsoft Office");
textRange1.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat1);
// Add regular content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange2 = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java is a totally independent Word component, Microsoft Office is not required in order to use Spire.Doc for Java.");
textRange2.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat2);
// Add a paragraph with Heading 3 style
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading_3);
textRange1 = paragraph.appendText("Word Versions");
textRange1.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat1);
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange2 = paragraph.appendText("Word97-03 Word2007 Word2010 Word2013 Word2016 Word2019");
textRange2.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat2);
// Add a paragraph with Heading 2 style
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading_2);
textRange1 = paragraph.appendText("High Quality File Conversion");
textRange1.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat1);
// Add regular content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange2 = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java allows converting popular file formats like HTML, RTF, ODT, TXT, WordML, WordXML to Word and exporting Word to commonly used file formats such as PDF, XPS, Image, EPUB, HTML, TXT, ODT, RTF, WordML, WordXML in high quality. Moreover, conversion between Doc and Docx is supported as well.");
textRange2.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat2);
// Add a paragraph with Heading 2 style
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading_2);
textRange1 = paragraph.appendText("Support a Rich Set of Word Elements");
textRange1.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat1);
// Add regular content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange2 = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java supports a rich set of Word elements, including section, header, footer, footnote, endnote, paragraph, list, table, text, TOC, form field, mail merge, hyperlink, bookmark, watermark, image, style, shape, textbox, ole, WordArt, background settings, digital signature, document encryption and many more.");
textRange2.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat2);
// Update the table of contents
doc.updateTableOfContents();
// Save the document
doc.saveToFile("Table of Contents Created Using Heading Styles.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Dispose of resources
doc.dispose();
}
}

Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Outline Level Styles
You can also use outline level styles to create a table of contents in a Word document. In Spire.Doc, by setting the OutlineLevel property of a paragraph, you can specify the hierarchical style of the paragraph in the outline. Then, by calling the TableOfContent.setTOCLevelStyle() method, you can apply these outline level styles to the generation rules of the table of contents. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.addSection() method.
- Create a ParagraphStyle object and set the outline level using ParagraphStyle.getParagraphFormat().setOutlineLevel(OutlineLevel.Level_1).
- Add the created ParagraphStyle object to the document using Document.getStyles().add() method.
- Add a paragraph using Section.addParagraph() method.
- Create a table of contents object using Paragraph.appendTOC(int lowerLevel, int upperLevel) method.
- Set the default setting for creating the table of contents using heading styles to false, TableOfContent.setUseHeadingStyles(false).
- Apply the outline level styles to the table of contents rules using TableOfContent.setTOCLevelStyle(int levelNumber, string styleName) method.
- Create a CharacterFormat object and set the font.
- Apply the style to the paragraph using Paragraph.applyStyle(ParagraphStyle.getName()) method.
- Add text content using Paragraph.appendText() method.
- Apply character formatting to the text using TextRange.applyCharacterFormat() method.
- Update the table of contents using Document.updateTableOfContents() method.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import com.spire.doc.formatting.*;
public class CreateTOCByOutlineLevelStyle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
Section section = doc.addSection();
// Define Outline Level 1
ParagraphStyle titleStyle1 = new ParagraphStyle(doc);
titleStyle1.setName("T1S");
titleStyle1.getParagraphFormat().setOutlineLevel(OutlineLevel.Level_1);
titleStyle1.getCharacterFormat().setBold(true);
titleStyle1.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
titleStyle1.getCharacterFormat().setFontSize(18f);
titleStyle1.getParagraphFormat().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.Left);
doc.getStyles().add(titleStyle1);
// Define Outline Level 2
ParagraphStyle titleStyle2 = new ParagraphStyle(doc);
titleStyle2.setName("T2S");
titleStyle2.getParagraphFormat().setOutlineLevel(OutlineLevel.Level_2);
titleStyle2.getCharacterFormat().setBold(true);
titleStyle2.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
titleStyle2.getCharacterFormat().setFontSize(16f);
titleStyle2.getParagraphFormat().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.Left);
doc.getStyles().add(titleStyle2);
// Define Outline Level 3
ParagraphStyle titleStyle3 = new ParagraphStyle(doc);
titleStyle3.setName("T3S");
titleStyle3.getParagraphFormat().setOutlineLevel(OutlineLevel.Level_3);
titleStyle3.getCharacterFormat().setBold(true);
titleStyle3.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
titleStyle3.getCharacterFormat().setFontSize(14f);
titleStyle3.getParagraphFormat().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.Left);
doc.getStyles().add(titleStyle3);
// Add Table of Contents paragraph
Paragraph TOCparagraph = section.addParagraph();
TableOfContent toc = TOCparagraph.appendTOC(1, 3);
toc.setUseHeadingStyles(false);
toc.setUseHyperlinks(true);
toc.setUseTableEntryFields(false);
toc.setRightAlignPageNumbers(true);
toc.setTOCLevelStyle(1, titleStyle1.getName());
toc.setTOCLevelStyle(2, titleStyle2.getName());
toc.setTOCLevelStyle(3, titleStyle3.getName());
// Define Character Format
CharacterFormat characterFormat = new CharacterFormat(doc);
characterFormat.setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
characterFormat.setFontSize(12);
// Add paragraph and apply Outline Level Style 1
Paragraph paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(titleStyle1.getName());
paragraph.appendText("Overview");
// Add paragraph and set text content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
TextRange textRange = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java is a professional Word API that empowers Java applications to create, convert, manipulate and print Word documents without dependency on Microsoft Word.");
textRange.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat);
// Add paragraph and apply Outline Level Style 1
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(titleStyle1.getName());
paragraph.appendText("MAIN FUNCTION");
// Add paragraph and apply Outline Level Style 2
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(titleStyle2.getName());
paragraph.appendText("Only Spire.Doc for Java, No Microsoft Office");
// Add paragraph and set text content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java is a totally independent Word component, Microsoft Office is not required in order to use Spire.Doc for Java.");
textRange.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat);
// Add paragraph and apply Outline Level Style 3
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(titleStyle3.getName());
paragraph.appendText("Word Versions");
// Add paragraph and set text content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange = paragraph.appendText("Word97-03 Word2007 Word2010 Word2013 Word2016 Word2019");
textRange.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat);
// Add paragraph and apply Outline Level Style 2
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(titleStyle2.getName());
paragraph.appendText("High Quality File Conversion");
// Add paragraph and set text content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java allows converting popular file formats like HTML, RTF, ODT, TXT, WordML, WordXML to Word and exporting Word to commonly used file formats such as PDF, XPS, Image, EPUB, HTML, TXT, ODT, RTF, WordML, WordXML in high quality. Moreover, conversion between Doc and Docx is supported as well.");
textRange.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat);
// Add paragraph and apply Outline Level Style 2
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
paragraph.applyStyle(titleStyle2.getName());
paragraph.appendText("Support a Rich Set of Word Elements");
// Add paragraph and set text content
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
textRange = paragraph.appendText("Spire.Doc for Java supports a rich set of Word elements, including section, header, footer, footnote, endnote, paragraph, list, table, text, TOC, form field, mail merge, hyperlink, bookmark, watermark, image, style, shape, textbox, ole, WordArt, background settings, digital signature, document encryption and many more.");
textRange.applyCharacterFormat(characterFormat);
// Update the table of contents
doc.updateTableOfContents();
// Save the document
doc.saveToFile("Creating Table of Contents with Outline Level Styles.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Dispose of resources
doc.dispose();
}
}

Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Image Captions
Using the Spire.Doc library, you can create a table of contents based on image titles using the TableOfContent tocForImage = new TableOfContent(Document, " \\h \\z \\c \"Image\"") method. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.addSection() method.
- Create a table of contents object TableOfContent tocForImage = new TableOfContent(Document, " \\h \\z \\c \"Image\"") and specify the style of the table of contents.
- Add a paragraph using the Section.addParagraph() method.
- Add the table of contents object to the paragraph using the Paragraph.getItems().add(tocForImage) method.
- Add a field separator using the Paragraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_Separator) method.
- Add the text content "TOC" using the Paragraph.appendText("TOC") method.
- Add a field end mark using the Paragraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_End) method.
- Add an image using the Paragraph.appendPicture() method.
- Add a paragraph for the image title, including product information and formatting, using the DocPicture.addCaption() method.
- Update the table of contents to reflect changes in the document using the Document.updateTableOfContents(tocForImage) method.
- Save the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
public class CreateTOCByImageCaption {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Add a section to the document
Section section = doc.addSection();
// Create a table of content object for images
TableOfContent tocForImage = new TableOfContent(doc, " \\h \\z \\c \"Images\"");
// Add a paragraph to the section
Paragraph tocParagraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
// Add the table of content object to the paragraph
tocParagraph.getItems().add(tocForImage);
// Add a field separator
tocParagraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_Separator);
// Add text content
tocParagraph.appendText("TOC");
// Add a field end mark
tocParagraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_End);
// Add a blank paragraph to the section
section.getBody().addParagraph();
// Add a paragraph to the section
Paragraph paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
// Add an image
DocPicture docPicture = paragraph.appendPicture("images/Doc-Java.png");
docPicture.setWidth(100);
docPicture.setHeight(100);
// Add a paragraph for the image caption
Paragraph pictureCaptionParagraph = (Paragraph) docPicture.addCaption("Images", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.Below_Item);
pictureCaptionParagraph.appendText(" Spire.Doc for Java Product ");
pictureCaptionParagraph.getFormat().setAfterSpacing(20);
// Continue adding paragraphs to the section
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
docPicture = paragraph.appendPicture("images/PDF-Java.png");
docPicture.setWidth(100);
docPicture.setHeight(100);
pictureCaptionParagraph = (Paragraph) docPicture.addCaption("Images", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.Below_Item);
pictureCaptionParagraph.appendText(" Spire.PDF for Java Product ");
pictureCaptionParagraph.getFormat().setAfterSpacing(20);
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
docPicture = paragraph.appendPicture("images/XLS-Java.png");
docPicture.setWidth(100);
docPicture.setHeight(100);
pictureCaptionParagraph = (Paragraph) docPicture.addCaption("Images", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.Below_Item);
pictureCaptionParagraph.appendText(" Spire.XLS for Java Product ");
pictureCaptionParagraph.getFormat().setAfterSpacing(20);
paragraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
docPicture = paragraph.appendPicture("images/PPT-Java.png");
docPicture.setWidth(100);
docPicture.setHeight(100);
pictureCaptionParagraph = (Paragraph) docPicture.addCaption("Images", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.Below_Item);
pictureCaptionParagraph.appendText(" Spire.Presentation for Java Product ");
// Update the table of contents
doc.updateTableOfContents(tocForImage);
// Save the document to a file
doc.saveToFile("CreateTOCWithImageCaptions.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Dispose of the document object
doc.dispose();
}
}

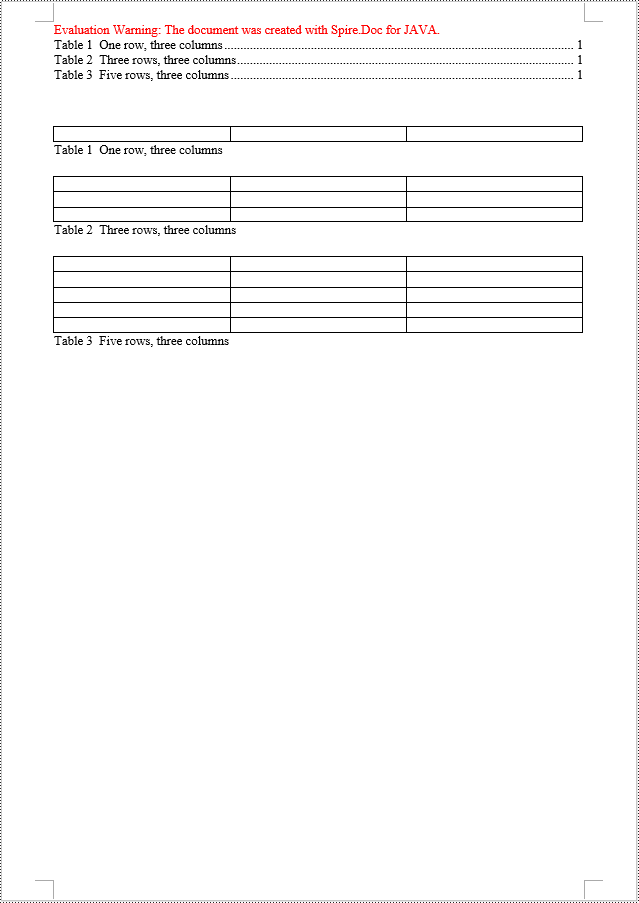
Java Create a Table Of Contents Using Table Captions
You can also create a table of contents using table titles by the method TableOfContent tocForImage = new TableOfContent(Document, " \\h \\z \\c \"Table\""). Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.addSection() method.
- Create a table of contents object TableOfContent tocForTable = new TableOfContent(Document, " \\h \\z \\c \"Table\"") and specify the style of the table of contents.
- Add a paragraph using the Section.addParagraph() method.
- Add the table of contents object to the paragraph using the Paragraph.getItems().add(tocForTable) method.
- Add a field separator using the Paragraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_Separator) method.
- Add the text "TOC" using the Paragraph.appendText("TOC") method.
- Add a field end mark using the Paragraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_End) method.
- Add a table using the Section.addTable() method and set the number of rows and columns using the Table.resetCells(int rowsNum, int columnsNum) method.
- Add a caption paragraph to the table using the Table.addCaption() method, including product information and formatting.
- Update the table of contents to reflect changes in the document using the Document.updateTableOfContents(tocForTable) method.
- Save the document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
public class CreateTOCByTableCaption {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document
Document doc = new Document();
// Add a section to the document
Section section = doc.addSection();
// Create a table of content object
TableOfContent tocForTable = new TableOfContent(doc, " \\h \\z \\c \"Table\"");
// Add a paragraph in the section to place the table of content
Paragraph tocParagraph = section.getBody().addParagraph();
tocParagraph.getItems().add(tocForTable);
tocParagraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_Separator);
tocParagraph.appendText("TOC");
tocParagraph.appendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.Field_End);
// Add two empty paragraphs in the section
section.getBody().addParagraph();
section.getBody().addParagraph();
// Add a table in the section
Table table = section.getBody().addTable(true);
table.resetCells(1, 3);
// Add a title for the table
Paragraph tableCaptionParagraph = (Paragraph) table.addCaption("Table", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.Below_Item);
tableCaptionParagraph.appendText(" One row, three columns");
tableCaptionParagraph.getFormat().setAfterSpacing(18);
// Add a new table in the section
table = section.getBody().addTable(true);
table.resetCells(3, 3);
// Add a title for the second table
tableCaptionParagraph = (Paragraph) table.addCaption("Table", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.Below_Item);
tableCaptionParagraph.appendText(" Three rows, three columns");
tableCaptionParagraph.getFormat().setAfterSpacing(18);
// Add another new table in the section
table = section.getBody().addTable(true);
table.resetCells(5, 3);
// Add a title for the third table
tableCaptionParagraph = (Paragraph) table.addCaption("Table", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.Below_Item);
tableCaptionParagraph.appendText(" Five rows, three columns");
// Update the table of contents
doc.updateTableOfContents(tocForTable);
// Save the document to a specified file
doc.saveToFile("CreateTableOfContentsUsingTableCaptions.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2016);
// Dispose of resources
doc.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Read Content from a Word Document
Extracting content from Word documents plays a crucial role in both work and study. Extracting one page of content helps in quickly browsing and summarizing key points, while extracting content from one section aids in in-depth study of specific topics or sections. Extracting the entire document allows you to have a comprehensive understanding of the document content, facilitating deep analysis and comprehensive comprehension. This article will introduce how to use Spire.Doc for Java to read a page, a section, and the entire content of a Word document in a Java project.
- Read a Page from a Word Document in Java
- Read a Section from a Word Document in Java
- Read the Entire Content from a Word Document in Java
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
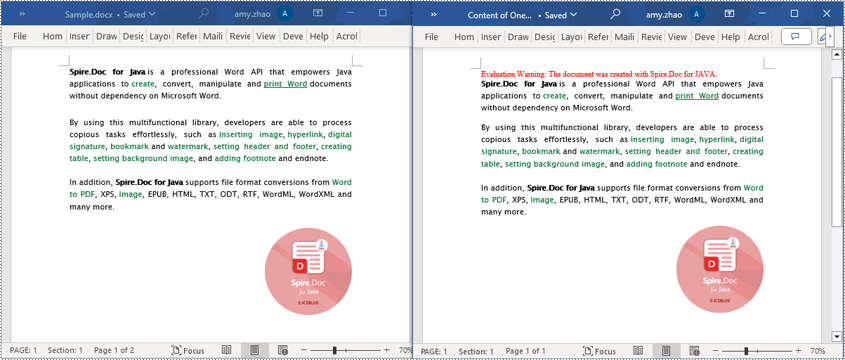
Read a Page from a Word Document in Java
Using the FixedLayoutDocument class and FixedLayoutPage class makes it easy to extract content from a specified page. To facilitate viewing the extracted content, the following example code saves the extracted content to a new Word document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Obtain a FixedLayoutPage object for a page in the document.
- Use the FixedLayoutPage.getSection() method to get the section where the page is located.
- Get the index position of the first paragraph on the page within the section.
- Get the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Create another Document object.
- Add a new section using Document.addSection().
- Clone the properties of the original section to the new section using Section.cloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection) method.
- Copy the content of the page from the original document to the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.pages.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
public class ReadOnePage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load document content from the specified file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the first page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.getPages().get(0);
// Get the section where the page is located
Section section = page.getSection();
// Get the first paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphStart = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getFirst().getParagraph();
int startIndex = 0;
if (paragraphStart != null) {
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
startIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphStart);
}
// Get the last paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getLast().getParagraph();
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null) {
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
endIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Add a new section
Section newSection = newdoc.addSection();
// Clone the properties of the original section to the new section
section.cloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection);
// Copy the content of the original document's page to the new document
for (int i = startIndex; i <=endIndex; i++)
{
newSection.getBody().getChildObjects().add(section.getBody().getChildObjects().get(i).deepClone());
}
// Save the new document to the specified file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of One Page.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
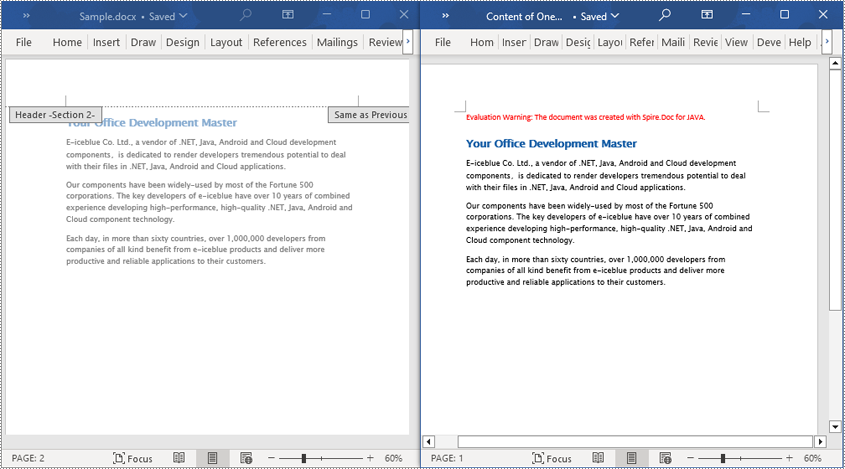
Read a Section from a Word Document in Java
Using Document.Sections[index], you can access specific Section objects that contain the header, footer, and body content of a document. The following example demonstrates a simple method to copy all content from one section to another document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Use Document.getSections().get(1) to retrieve the second section of the document.
- Create another new Document object.
- Clone the default style of the original document to the new document using Document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method.
- Use Document.getSections().add(section.deepClone()) to clone the content of the second section of the original document to the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
public class ReadOneSection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the second section of the document
Section section = document.getSections().get(1);
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Clone the second section to the new document
newdoc.getSections().add(section.deepClone());
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of One Section.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
Read the Entire Content from a Word Document in Java
This example demonstrates how to iterate through each section of the original document to read the entire content of the document and clone each section into a new document. This method can help you quickly replicate both the structure and content of the entire document, preserving the format and layout of the original document in the new document. Such operations are very useful for maintaining the integrity and consistency of the document structure. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create another new Document object.
- Clone the default style of the original document to the new document using the Document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method.
- Iterate through each section of the original document using a for loop and clone it into the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
public class ReadOneDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Iterate through each section in the original document and clone it to the new document
for (Section sourceSection : (Iterable) document.getSections()) {
newdoc.getSections().add(sourceSection.deepClone());
}
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of the entire document.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Add, Insert, or Delete Pages in Word Documents
Adding, inserting, and deleting pages in a Word document are crucial steps in managing and presenting content. By adding or inserting new pages, you can expand the document to accommodate more content, making it more organized and readable. Deleting pages helps simplify the document by removing unnecessary or erroneous information. These operations can enhance the overall quality and clarity of the document. This article will demonstrate how to use Spire.Doc for Java to add, insert, and delete pages in a Word document within a Java project.
- Add a Page in a Word Document in Java
- Insert a Page in a Word Document in Java
- Delete a Page from a Word Document in Java
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add a Page in a Word Document in Java
The steps to add a new page at the end of a Word document include locating the last section, and then inserting a page break at the end of that section's last paragraph. This way ensures that any content added subsequently will start displaying on a new page, maintaining the clarity and coherence of the document structure. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of the last section of the document using Document.getLastSection().getBody().
- Add a page break by calling Paragraph.appendBreak(BreakType.Page_Break) method.
- Create a new paragraph style ParagraphStyle object.
- Add the new paragraph style to the document's style collection using Document.getStyles().add(paragraphStyle) method.
- Create a new paragraph Paragraph object and set the text content.
- Apply the previously created paragraph style to the new paragraph using Paragraph.applyStyle(paragraphStyle.getName()) method.
- Add the new paragraph to the document using Body.getChildObjects().add(paragraph) method.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
public class AddOnePage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a sample document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the body of the last section of the document
Body body = document.getLastSection().getBody();
// Insert a page break after the last paragraph in the body
body.getLastParagraph().appendBreak(BreakType.Page_Break);
// Create a new paragraph style
ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle = new ParagraphStyle(document);
paragraphStyle.setName("CustomParagraphStyle1");
paragraphStyle.getParagraphFormat().setLineSpacing(12);
paragraphStyle.getParagraphFormat().setAfterSpacing(8);
paragraphStyle.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
paragraphStyle.getCharacterFormat().setFontSize(12);
// Add the paragraph style to the document's style collection
document.getStyles().add(paragraphStyle);
// Create a new paragraph and set the text content
Paragraph paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.appendText("Thank you for using our Spire.Doc for Java product. The trial version will add a red watermark to the generated result document and only supports converting the first 10 pages to other formats. Upon purchasing and applying a license, these watermarks will be removed, and the functionality restrictions will be lifted.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.applyStyle(paragraphStyle.getName());
// Add the paragraph to the body's content collection
body.getChildObjects().add(paragraph);
// Create another new paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.appendText("To fully experience our product, we provide a one-month temporary license for each of our customers for free. Please send an email to sales@e-iceblue.com, and we will send the license to you within one working day.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.applyStyle(paragraphStyle.getName());
// Add the paragraph to the body's content collection
body.getChildObjects().add(paragraph);
// Save the document to a specified path
document.saveToFile("Add a Page.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close the document
document.close();
// Dispose of the document object's resources
document.dispose();
}
}
Insert a Page in a Word Document in Java
Before inserting a new page, it is necessary to determine the ending position index of the specified page content within the section, and then add the content of the new page to the document one by one. To ensure that the content is separated from the subsequent pages, page breaks need to be inserted at appropriate positions. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Obtain the FixedLayoutPage object of a page in the document.
- Get the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Create a new paragraph style ParagraphStyle object.
- Add the new paragraph style to the document using the Document.getStyles().add(paragraphStyle) method.
- Create a new paragraph Paragraph object and set the text content.
- Apply the previously created paragraph style to the new paragraph using the Paragraph.applyStyle(paragraphStyle.getName()) method.
- Insert the new paragraph at the specified position using the Body.getChildObjects().insert(index, Paragraph) method.
- Create another new paragraph object, set its text content, add a page break by calling the Paragraph.appendBreak(BreakType.Page_Break) method, apply the previously created paragraph style, and finally insert this paragraph into the document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.pages.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
public class InsertOnePage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a sample document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the first page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.getPages().get(0);
// Get the body of the document
Body body = page.getSection().getBody();
// Get the paragraph at the end of the current page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getLast().getParagraph();
// Initialize the end index
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null) {
// Get the index of the last paragraph
endIndex = body.getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Create a new paragraph style
ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle = new ParagraphStyle(document);
paragraphStyle.setName("CustomParagraphStyle1");
paragraphStyle.getParagraphFormat().setLineSpacing(12);
paragraphStyle.getParagraphFormat().setAfterSpacing(8);
paragraphStyle.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Microsoft YaHei");
paragraphStyle.getCharacterFormat().setFontSize(12);
// Add the style to the document
document.getStyles().add(paragraphStyle);
// Create a new paragraph and set the text content
Paragraph paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.appendText("Thank you for using our Spire.Doc for Java product. The trial version will add a red watermark to the generated result document and only supports converting the first 10 pages to other formats. Upon purchasing and applying a license, these watermarks will be removed, and the functionality restrictions will be lifted.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.applyStyle(paragraphStyle.getName());
// Insert the paragraph at the specified position
body.getChildObjects().insert(endIndex + 1, paragraph);
// Create another new paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = new Paragraph(document);
paragraph.appendText("To fully experience our product, we provide a one-month temporary license for each of our customers for free. Please send an email to sales@e-iceblue.com, and we will send the license to you within one working day.");
// Apply the paragraph style
paragraph.applyStyle(paragraphStyle.getName());
// Add a page break
paragraph.appendBreak(BreakType.Page_Break);
// Insert the paragraph at the specified position
body.getChildObjects().insert(endIndex + 2, paragraph);
// Save the document to a specified path
document.saveToFile("Insert a New Page after a Specified Page.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and dispose of the document object's resources
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}

Delete a Page from a Word Document in Java
To delete the content of a page, you first need to find the position index of the starting and ending elements of that page in the document. Then, by looping through, you can remove these elements one by one to delete the entire content of the page. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Obtain the FixedLayoutPage object of the first page in the document.
- Use the FixedLayoutPage.getSection() method to get the section where the page is located.
- Get the index position of the first paragraph on the page within the section.
- Get the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Use a for loop to remove the content of the page one by one.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.pages.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
public class RemoveOnePage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a sample document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the second page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.getPages().get(1);
// Get the section of the page
Section section = page.getSection();
// Get the first paragraph on the first page
Paragraph paragraphStart = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getFirst().getParagraph();
int startIndex = 0;
if (paragraphStart != null) {
// Get the index of the starting paragraph
startIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphStart);
}
// Get the last paragraph on the last page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getLast().getParagraph();
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null) {
// Get the index of the ending paragraph
endIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Remove paragraphs within the specified range
for (int i = 0; i <= (endIndex - startIndex); i++) {
section.getBody().getChildObjects().removeAt(startIndex);
}
// Save the document to a specified path
document.saveToFile("Delete a Page.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and dispose of the document object's resources
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Add and Change Variables in Word Documents
Variables in Word documents are a type of field that is characterized by the ability of convenient and accurate text management, such as text replacement and deletion. Compared with the find-and-replace function, replacing text by assigning values to variables is faster and less error-prone. This article is going to show how to add or change variables in Word documents programmatically using Spire.Doc for Java.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Insert Variables into Word Documents
As variables are a kind of Word fields, we can use the Paragraph.appendField(String fieldName, FieldType.Field_Doc_Variable) method to insert variables into Word documents, and then use the VariableCollection.add() method to assign values to the variables. It should be noted that after assigning values to variables, document fields need to be updated to display the assigned values. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of Document.
- Add a section to the document using Document.addSection() method.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.addParagraph() method.
- Add variable fields to the paragraph using Paragraph.appendField(String fieldName, FieldType.Field_Doc_Variable) method.
- Get the variable collection using Document.getVariables() method.
- Assign a value to the variable using VariableCollection.add() method.
- Update the fields in the document using Document.isUpdateFields() method.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.formatting.CharacterFormat;
public class AddVariables {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create an object of Document
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.addSection();
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.addParagraph();
//Set text format
CharacterFormat characterFormat = paragraph.getStyle().getCharacterFormat();
characterFormat.setFontName("Times New Roman");
characterFormat.setFontSize(14);
//Set the page margin
section.getPageSetup().getMargins().setTop(80f);
//Add variable fields to the paragraph
paragraph.appendField("Term", FieldType.Field_Doc_Variable);
paragraph.appendText(" is an object.\r\n");
paragraph.appendField("Term", FieldType.Field_Doc_Variable);
paragraph.appendText(" is not a backdrop, an illusion, or an emergent phenomenon.\r\n");
paragraph.appendField("Term", FieldType.Field_Doc_Variable);
paragraph.appendText(" has a physical size that be measured in laboratories.");
//Get the variable collection
VariableCollection variableCollection = document.getVariables();
//Assign a value to the variable
variableCollection.add("Term", "Time");
//Update the fields in the document
document.isUpdateFields(true);
//Save the document
document.saveToFile("AddVariables.docx", FileFormat.Auto);
document.dispose();
}
}
Change the Value of Variables in Word Documents
Spire.Doc for Java provides the VariableCollection.set() method to change the values of variables. And after updating fields in the document, all the occurrences of the variables will display the newly assigned value, thus achieving fast and accurate text replacement. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of Document.
- Load a Word document using Document.loaFromFile() method.
- Get the variable collection using Document.getVariables() method.
- Assign a new value to a specific variable through its name using VariableCollection.set() method.
- Update the fields in the document using Document.isUpdateFields() method.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.VariableCollection;
public class ChangeVariableValue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create an object of Document
Document document = new Document();
//Load a Word document
document.loadFromFile("AddVariables.docx");
//Get the variable collection
VariableCollection variableCollection = document.getVariables();
//Assign a new value to a variable
variableCollection.set("Term", "The time");
//Update the fields in the document
document.isUpdateFields(true);
//Save the document
document.saveToFile("ChangeVariable.docx", FileFormat.Auto);
document.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Split Word Documents
When you have a fairly long Word document that requires teamwork, it may be necessary to split the document into several shorter files and assign them to different people to speed up the workflow. Instead of manually cutting and pasting, this article will demonstrate how to programmatically split a Word document using Spire.Doc for Java .
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Split a Word Document by Page Break
A Word document can contain multiple pages separated by page breaks. To split a Word document by page break, you can refer to the below steps and code.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a sample Word document using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a new Word document and add a section to it.
- Traverse through all body child objects of each section in the original document and determine whether the child object is a paragraph or a table.
- If the child object of the section is a table, directly add it to the section of new document using Section.getBody().getChildObjects().add() method.
- If the child object of the section is a paragraph, first add the paragraph object to the section of the new document. Then traverse through all child objects of the paragraph and determine whether the child object is a page break.
- If the child object is a page break, get its index and then remove the page break from its paragraph by index.
- Save the new Word document and then repeat the above processes.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
public class splitDocByPageBreak {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Create a Document instance
Document original = new Document();
// Load a sample Word document
original.loadFromFile("E:\\Files\\SplitByPageBreak.docx");
// Create a new Word document and add a section to it
Document newWord = new Document();
Section section = newWord.addSection();
int index = 0;
//Traverse through all sections of original document
for (int s = 0; s < original.getSections().getCount(); s++) {
Section sec = original.getSections().get(s);
//Traverse through all body child objects of each section.
for (int c = 0; c < sec.getBody().getChildObjects().getCount(); c++) {
DocumentObject obj = sec.getBody().getChildObjects().get(c);
if (obj instanceof Paragraph) {
Paragraph para = (Paragraph) obj;
sec.cloneSectionPropertiesTo(section);
//Add paragraph object in original section into section of new document
section.getBody().getChildObjects().add(para.deepClone());
for (int i = 0; i < para.getChildObjects().getCount(); i++) {
DocumentObject parobj = para.getChildObjects().get(i);
if (parobj instanceof Break) {
Break break1 = (Break) parobj;
if (break1.getBreakType().equals(BreakType.Page_Break)) {
//Get the index of page break in paragraph
int indexId = para.getChildObjects().indexOf(parobj);
//Remove the page break from its paragraph
Paragraph newPara = (Paragraph) section.getBody().getLastParagraph();
newPara.getChildObjects().removeAt(indexId);
//Save the new Word document
newWord.saveToFile("output/result"+index+".docx", FileFormat.Docx);
index++;
//Create a new document and add a section
newWord = new Document();
section = newWord.addSection();
//Add paragraph object in original section into section of new document
section.getBody().getChildObjects().add(para.deepClone());
if (section.getParagraphs().get(0).getChildObjects().getCount() == 0) {
//Remove the first blank paragraph
section.getBody().getChildObjects().removeAt(0);
} else {
//Remove the child objects before the page break
while (indexId >= 0) {
section.getParagraphs().get(0).getChildObjects().removeAt(indexId);
indexId--;
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (obj instanceof Table) {
//Add table object in original section into section of new document
section.getBody().getChildObjects().add(obj.deepClone());
}
}
}
//Save to file
newWord.saveToFile("output/result"+index+".docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
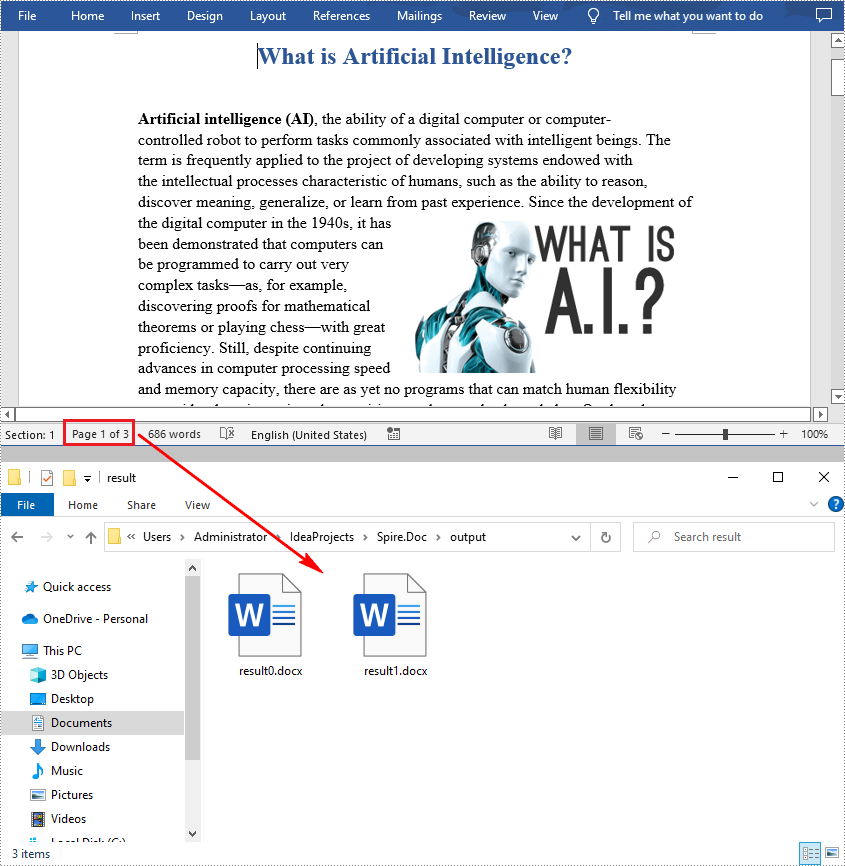
Split a Word Document by Section Break
In Word, a section is a part of a document that contains its own page formatting. For documents that contain multiple sections, Spire.Doc for .NET also supports splitting documents by section breaks. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a sample Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Define a new Word document object.
- Traverse through all sections of the original Word document.
- Clone each section of the original document using Section.deepClone() method.
- Add the cloned section to the new document as a new section using Document.getSections().add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
public class splitDocBySectionBreak {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create Document instance
Document document = new Document();
//Load a sample Word document
document.loadFromFile("E:\\Files\\SplitBySectionBreak.docx");
//Define a new Word document object
Document newWord;
//Traverse through all sections of the original Word document
for (int i = 0; i < document.getSections().getCount(); i++){
newWord = new Document();
//Clone each section of the original document and add it to the new document as new section
newWord.getSections().add(document.getSections().get(i).deepClone());
//Save the result document
newWord.saveToFile("Result/result"+i+".docx");
}
}
}
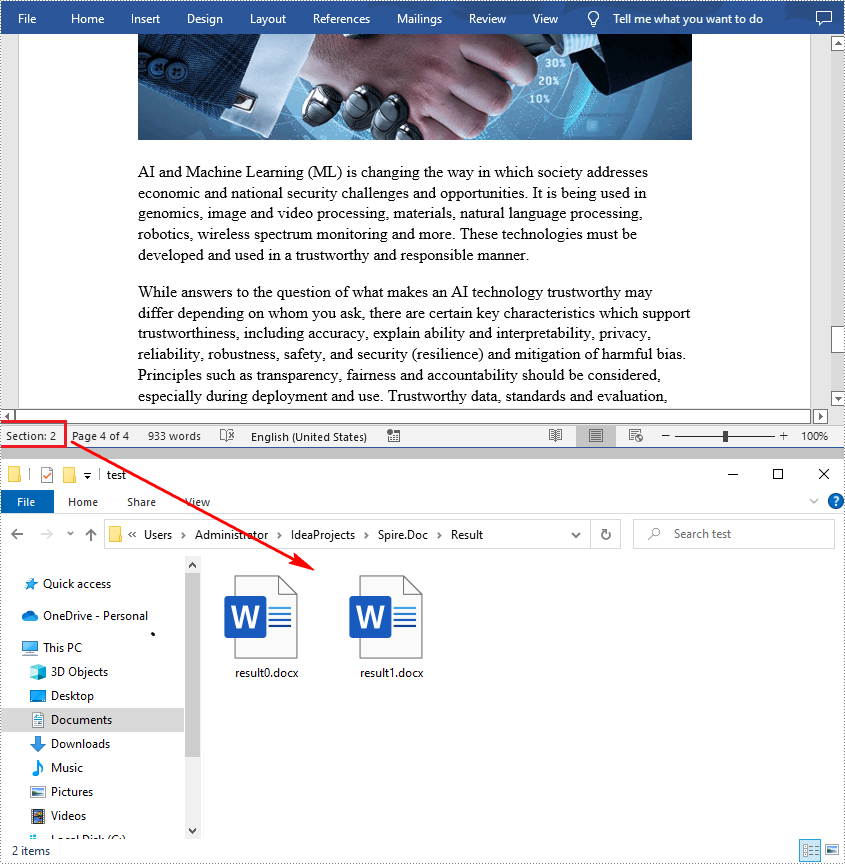
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Get All Revisions from Word
After you enable the Track Changes feature in a Word document, it records all the edits in the document, such as insertions, deletions, replacements, and format changes. Track Changes is a great feature allowing you to see what changes have been made to a document. This tutorial shows how to get all revisions from a Word document by using Spire.Doc for Java.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>12.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Get All Revisions from Word
The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document instance and load a sample Word document using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a StringBuilder object and then using StringBuilder.append() method to log data.
- Traverse all the sections and every element under body in the section.
- Determine if the paragraph is an insertion revision or not using Paragraph.isInsertRevision() method. If yes, use Paragraph.getInsertRevision() method to get the insertion revision. Then get the revision type and author using EditRevision.getType() method and EditRevision.getAuthor() method.
- Determine if the paragraph is a delete revision or not using Paragraph.inDeleteRevision() method. If yes, use Paragraph.getDeleteRevision() method to get the delete revision. Then get the revision type and author using EditRevision.getType() method and EditRevision.getAuthor() method.
- Traverse all the elements in the paragraphs to get the text ranges' revisions.
- Write the content of StringBuilder to a txt document using FileWriter.write() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import com.spire.doc.formatting.revisions.*;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class getRevisions {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Load the sample Word document
Document document = new Document();
document.loadFromFile("test file.docx");
//Create a StringBuilder object to get the insertions
StringBuilder insertRevision = new StringBuilder();
insertRevision.append("Insert revisions:"+"\n");
int index_insertRevision = 0;
//Create a StringBuilder object to get the deletions
StringBuilder deleteRevision = new StringBuilder();
deleteRevision.append("Delete revisions:"+"\n");
int index_deleteRevision = 0;
//Traverse all the sections
for (Section sec : (Iterable<Section>) document.getSections())
{
//Iterate through the element under body in the section
for(DocumentObject docItem : (Iterable<DocumentObject>)sec.getBody().getChildObjects())
{
if (docItem instanceof Paragraph)
{
Paragraph para = (Paragraph)docItem;
//Determine if the paragraph is an insertion revision
if (para.isInsertRevision())
{
index_insertRevision++;
insertRevision.append("Index: " + index_insertRevision+"\n");
//Get insertion revision
EditRevision insRevison = para.getInsertRevision();
//Get insertion revision type
EditRevisionType insType = insRevison.getType();
insertRevision.append("Type: " + insType+"\n");
//Get insertion revision author
String insAuthor = insRevison.getAuthor();
insertRevision.append("Author: " + insAuthor + "\n");
}
//Determine if the paragraph is a delete revision
else if (para.isDeleteRevision())
{
index_deleteRevision++;
deleteRevision.append("Index: " + index_deleteRevision +"\n");
EditRevision delRevison = para.getDeleteRevision();
EditRevisionType delType = delRevison.getType();
deleteRevision.append("Type: " + delType+ "\n");
String delAuthor = delRevison.getAuthor();
deleteRevision.append("Author: " + delAuthor + "\n");
}
//Iterate through the element in the paragraph
for(DocumentObject obj : (Iterable<DocumentObject>)para.getChildObjects())
{
if (obj instanceof TextRange)
{
TextRange textRange = (TextRange)obj;
//Determine if the textrange is an insertion revision
if (textRange.isInsertRevision())
{
index_insertRevision++;
insertRevision.append("Index: " + index_insertRevision +"\n");
EditRevision insRevison = textRange.getInsertRevision();
EditRevisionType insType = insRevison.getType();
insertRevision.append("Type: " + insType + "\n");
String insAuthor = insRevison.getAuthor();
insertRevision.append("Author: " + insAuthor + "\n");
}
else if (textRange.isDeleteRevision())
{
index_deleteRevision++;
deleteRevision.append("Index: " + index_deleteRevision +"\n");
//Determine if the textrange is a delete revision
EditRevision delRevison = textRange.getDeleteRevision();
EditRevisionType delType = delRevison.getType();
deleteRevision.append("Type: " + delType+"\n");
String delAuthor = delRevison.getAuthor();
deleteRevision.append("Author: " + delAuthor+"\n");
}
}
}
}
}
}
//Save to a .txt file
FileWriter writer1 = new FileWriter("insertRevisions.txt");
writer1.write(insertRevision.toString());
writer1.flush();
writer1.close();
//Save to a .txt file
FileWriter writer2 = new FileWriter("deleteRevisions.txt");
writer2.write(deleteRevision.toString());
writer2.flush();
writer2.close();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.