The Excel spreadsheet is extensively utilized for organizing, analyzing, and presenting data in a tabular format. The capacity to programmatically interact with Excel files holds great value as it facilitates automation and integration of Excel functionality within software applications. Specifically, knowing how to create new Excel documents, retrieve information from existing ones, and update or modify them as needed through code would be very helpful. This article will demonstrate how to create, read, or update Excel documents in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create an Excel Document in Python
- Read Data from a Worksheet in Python
- Update an Excel Document in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create an Excel Document in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers a variety of classes and interfaces that you can use to create and edit Excel documents. Here is a list of important classes, properties and methods involved in this article.
| Member | Description |
| Workbook class | Represents an Excel workbook model. |
| Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method | Adds a worksheet to workbook. |
| Workbook.SaveToFile() method | Saves the workbook to an Excel document. |
| Worksheet class | Represents a worksheet in a workbook. |
| Worksheet.Range property | Gets a specific cell or cell range from worksheet. |
| Worksheet.Range.Text property | Gets or sets the text value of a cell. |
| Worksheet.Rows property | Gets a collection of rows in worksheet. |
| CellRange class | Represents a cell or cell range in worksheet. |
The following are the steps to create an Excel document from scratch using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Add a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Write data to specific cells through Worksheet.Range.Text property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook()
# Remove default worksheets
wb.Worksheets.Clear()
# Add a worksheet and name it "Employee"
sheet = wb.Worksheets.Add("Employee")
# Merge the cells between A1 and G1
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Merge()
# Write data to A1 and apply formatting to it
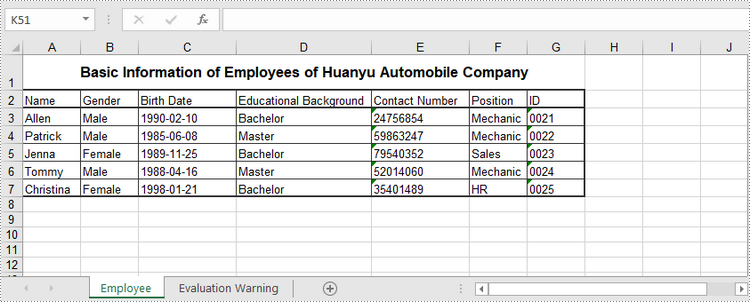
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Basic Information of Employees of Huanyu Automobile Company"
sheet.Range["A1"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.Size = 13
# Set row height of the first row
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 30
# Write data to specific cells
sheet.Range["A2"].Text = "Name"
sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "Gender"
sheet.Range["C2"].Text = "Birth Date"
sheet.Range["D2"].Text = "Educational Background"
sheet.Range["E2"].Text = "Contact Number"
sheet.Range["F2"].Text = "Position"
sheet.Range["G2"].Text = "ID"
sheet.Range["A3"].Text = "Allen"
sheet.Range["B3"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C3"].Text = "1990-02-10"
sheet.Range["D3"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E3"].Text = "24756854"
sheet.Range["F3"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G3"].Text = "0021"
sheet.Range["A4"].Text = "Patrick"
sheet.Range["B4"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C4"].Text = "1985-06-08"
sheet.Range["D4"].Text = "Master"
sheet.Range["E4"].Text = "59863247"
sheet.Range["F4"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G4"].Text = "0022"
sheet.Range["A5"].Text = "Jenna"
sheet.Range["B5"].Text = "Female"
sheet.Range["C5"].Text = "1989-11-25"
sheet.Range["D5"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E5"].Text = "79540352"
sheet.Range["F5"].Text = "Sales"
sheet.Range["G5"].Text = "0023"
sheet.Range["A6"].Text = "Tommy"
sheet.Range["B6"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C6"].Text = "1988-04-16"
sheet.Range["D6"].Text = "Master"
sheet.Range["E6"].Text = "52014060"
sheet.Range["F6"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G6"].Text = "0024"
sheet.Range["A7"].Text = "Christina"
sheet.Range["B7"].Text = "Female"
sheet.Range["C7"].Text = "1998-01-21"
sheet.Range["D7"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E7"].Text = "35401489"
sheet.Range["F7"].Text = "HR"
sheet.Range["G7"].Text = "0025"
# Set row height of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].RowHeight = 15
# Set column width
sheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 15)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(4, 21)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(5, 15)
# Set border style of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium)
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin)
sheet.Range["A2:G2"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium)
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].Borders.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Black
# Save to a .xlsx file
wb.SaveToFile("output/NewSpreadsheet.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
Read Data from a Worksheet in Python
The Worksheet.Range.Value property returns number value or text value of a cell as a string. To get data of a whole worksheet or a cell range, loop through the cells within it. The following are the steps to get data of a worksheet using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the cell range contain data though Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Iterate through the rows and columns to get cells within the range, and return the value of each cell through CellRange.Value property.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx");
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]
# Get the cell range containing data
locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Iterate through the rows
for i in range(len(sheet.Rows)):
# Iterate through the columns
for j in range(len(locatedRange.Rows[i].Columns)):
# Get data of a specific cell
print(locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value + " ", end='')
print("")

Update an Excel Document in Python
To change the value of a certain cell, just re-assign a value to it through Worksheet.Range.Value property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Change the value of a particular cell though Worksheet.Range.Value property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook();
# Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]
# Change the value of a specific cell
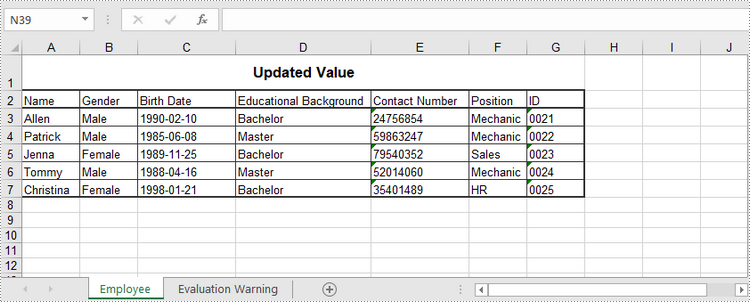
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Updated Value"
# Save to file
wb.SaveToFile("output/Updated.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.